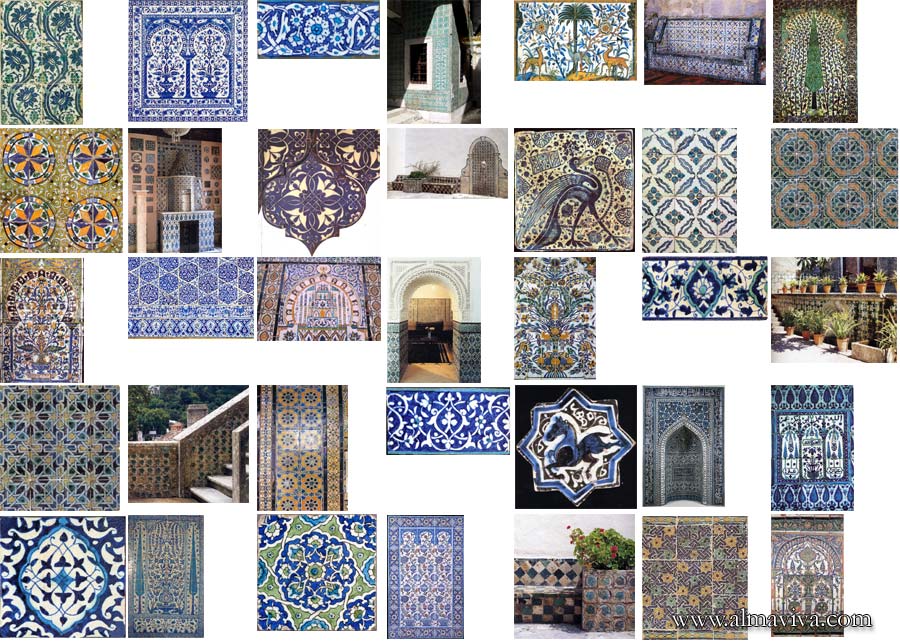
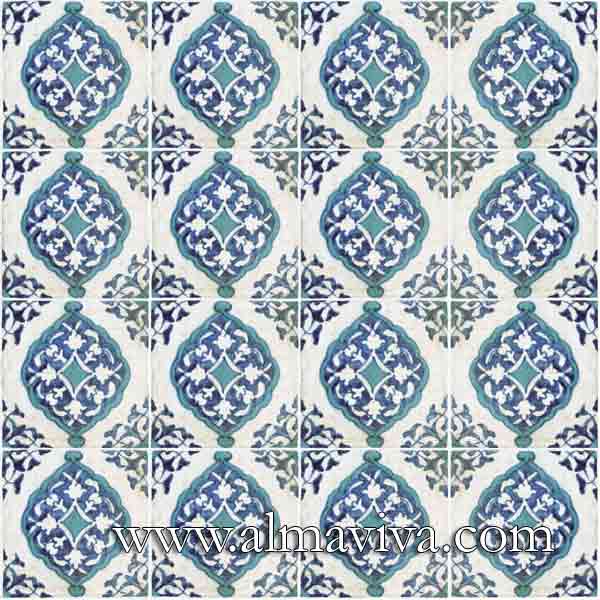
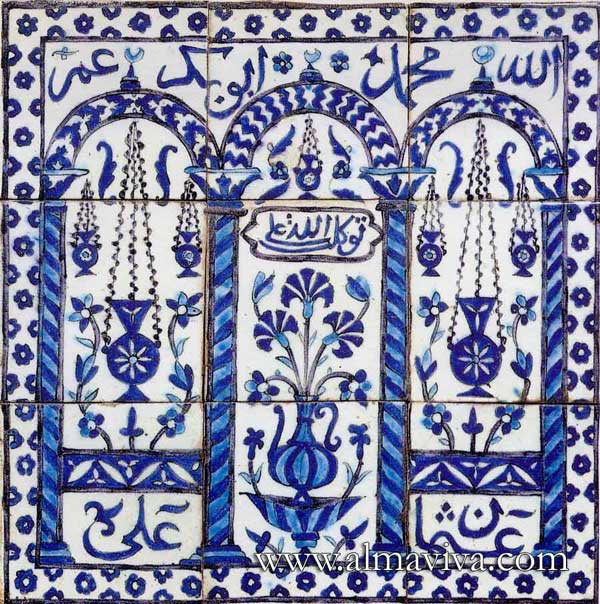
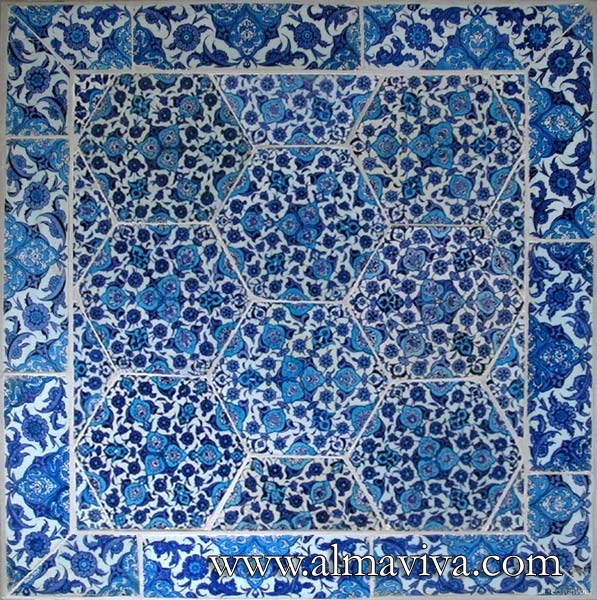
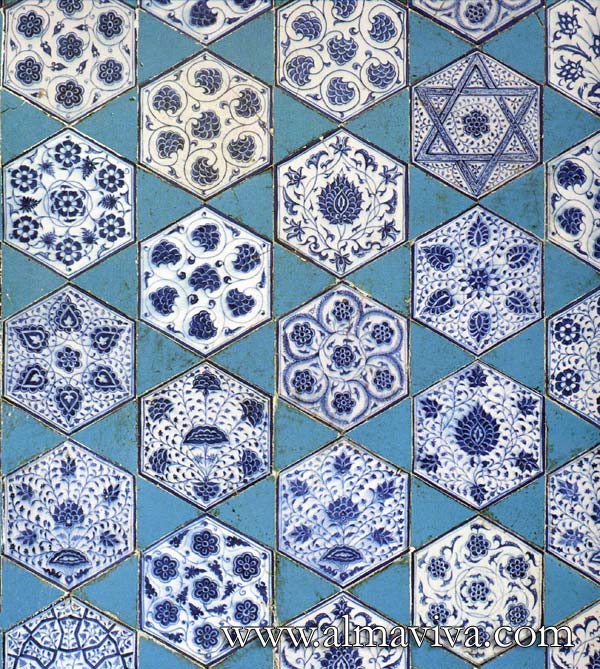
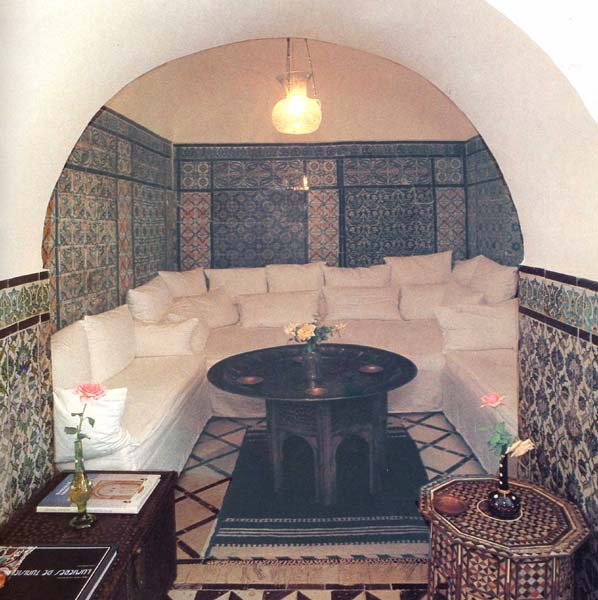
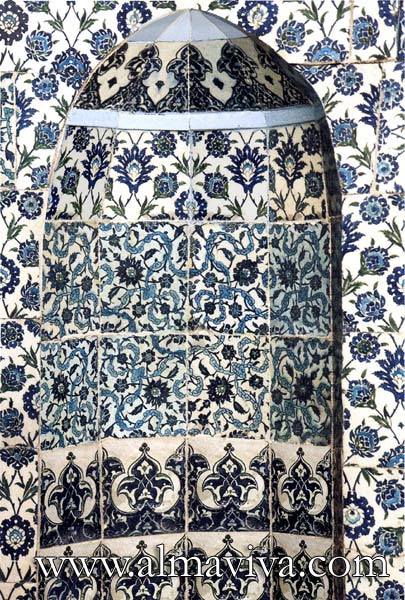
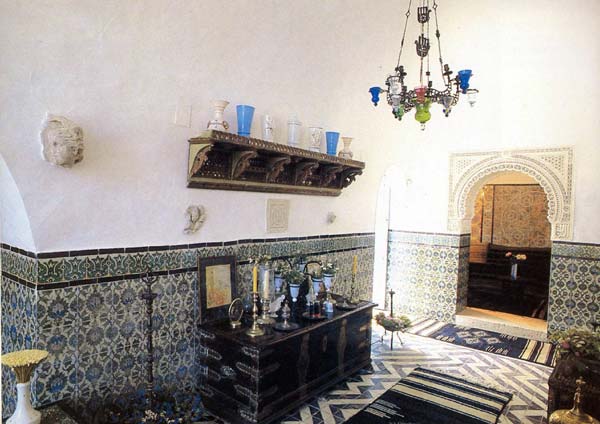
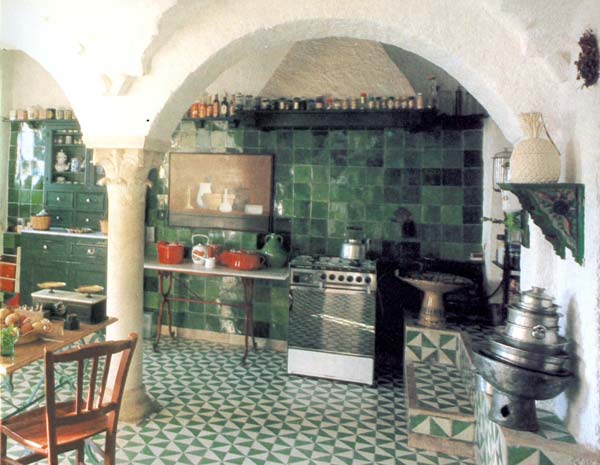
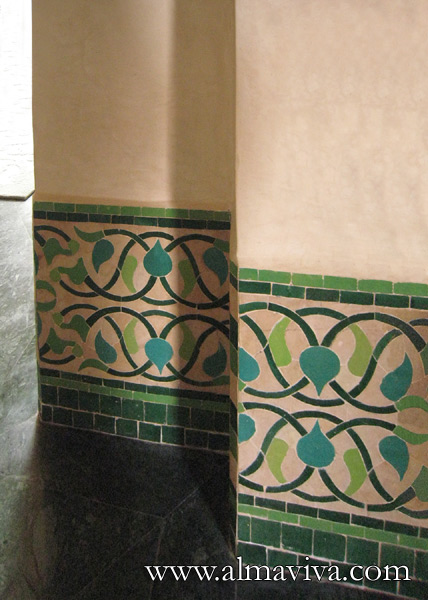
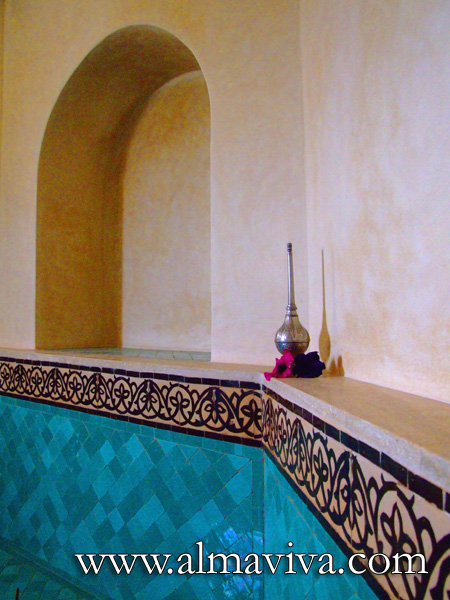
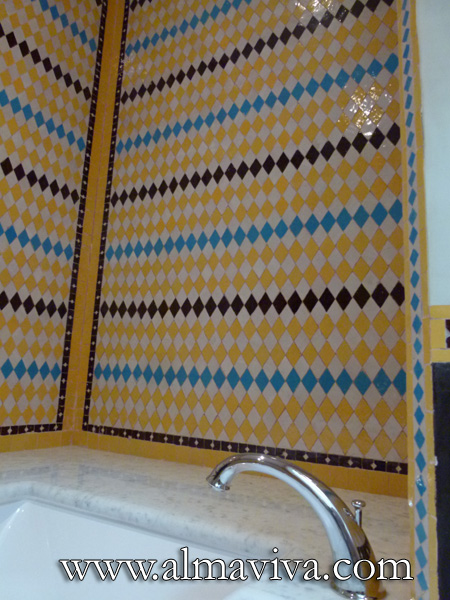
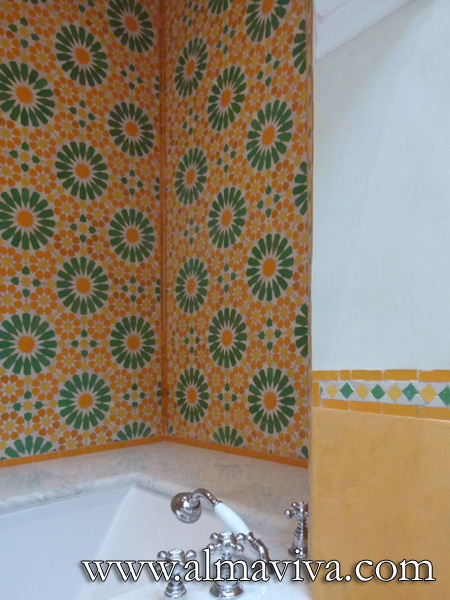
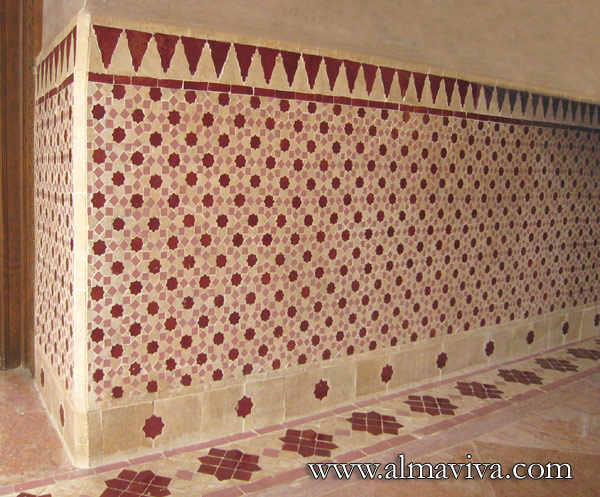
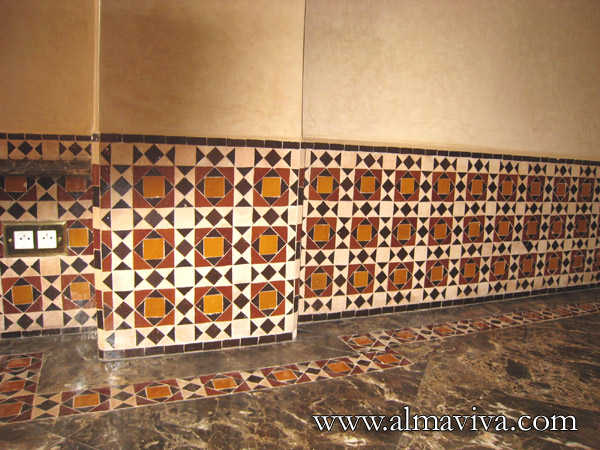
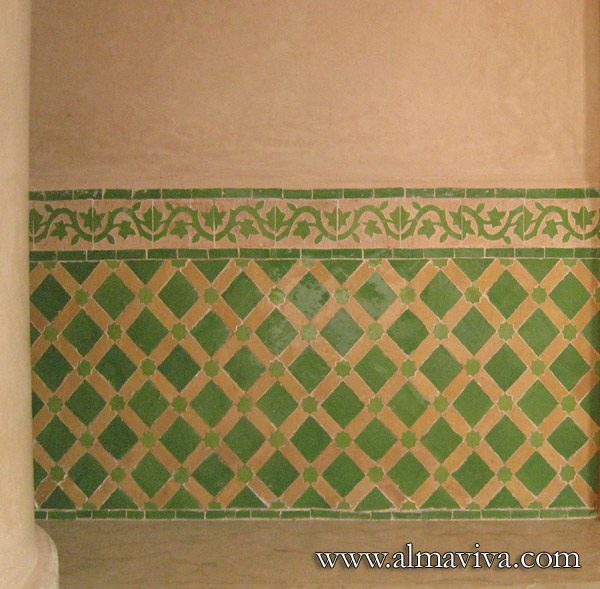
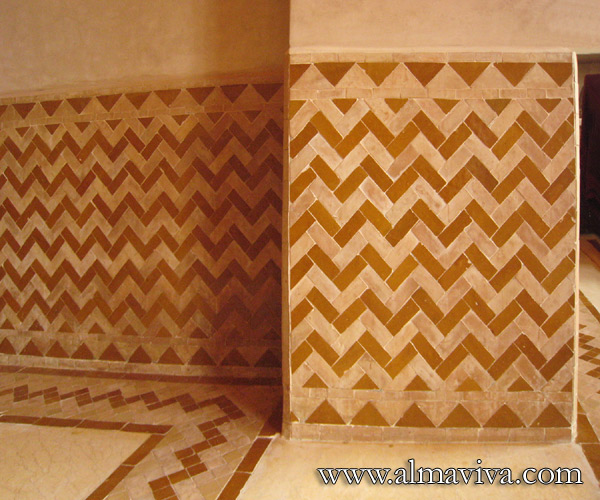
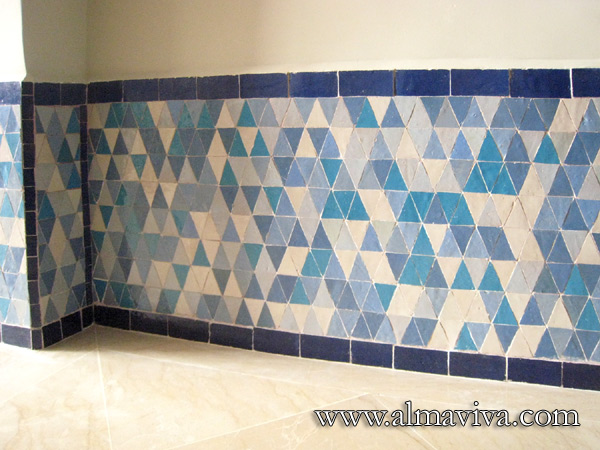
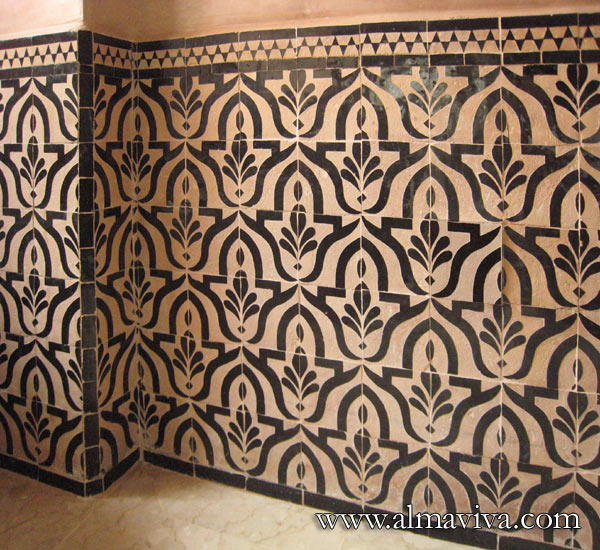
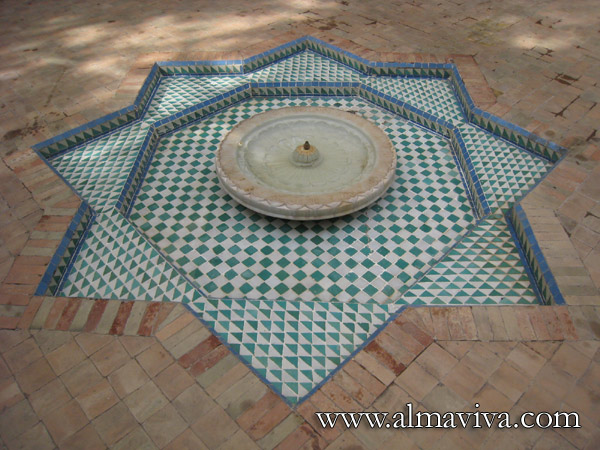
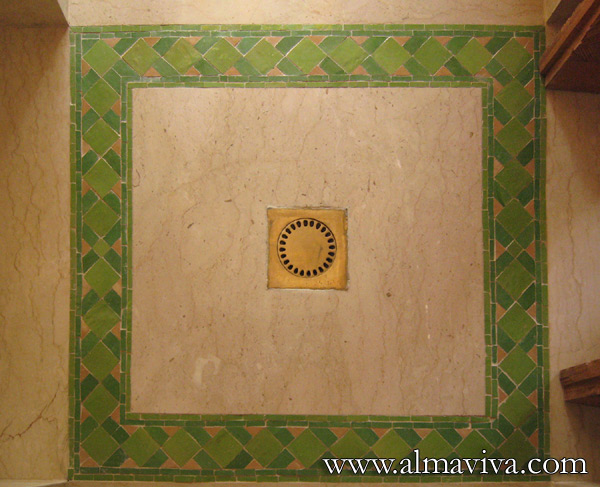
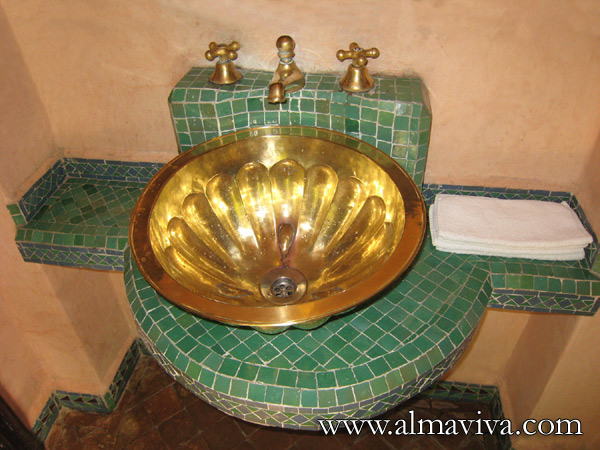
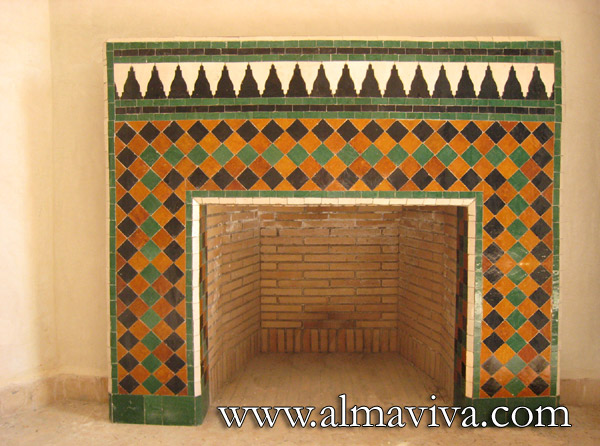
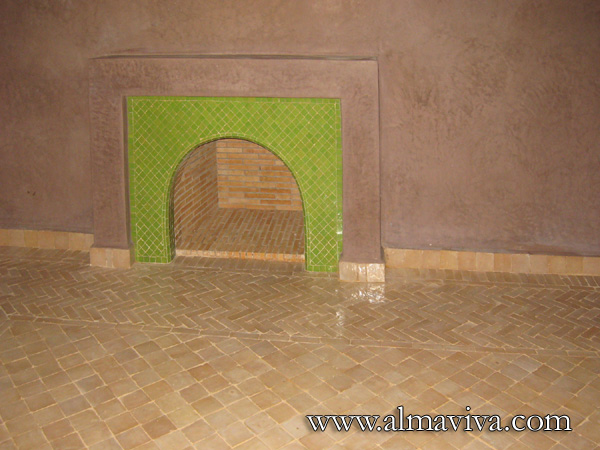
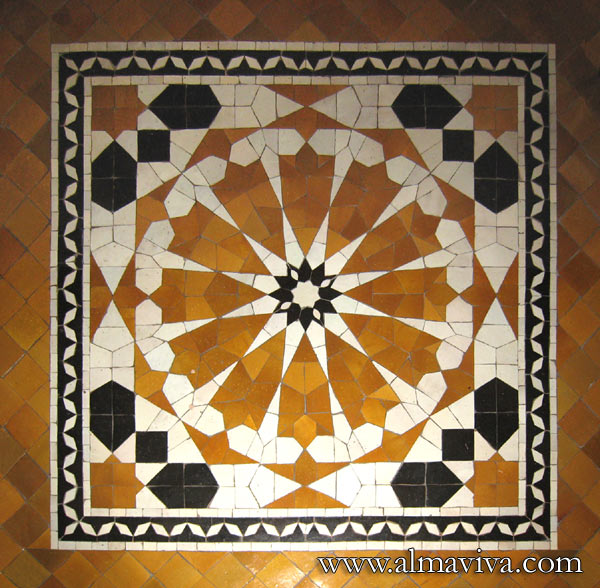
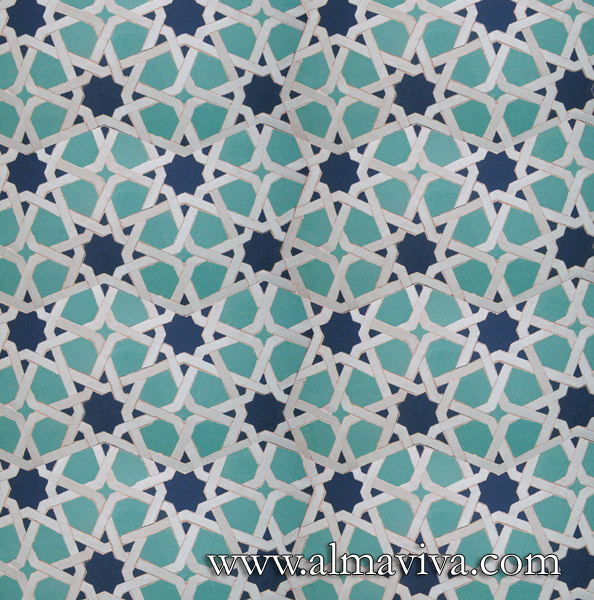
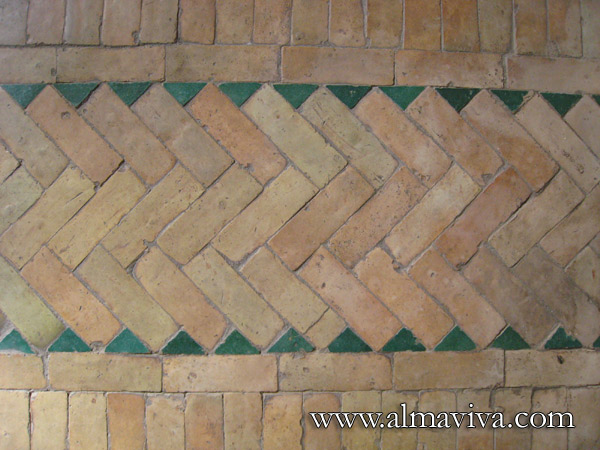
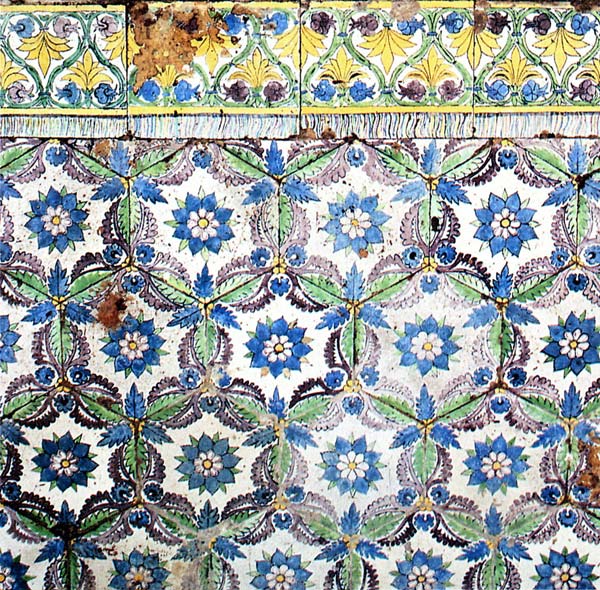
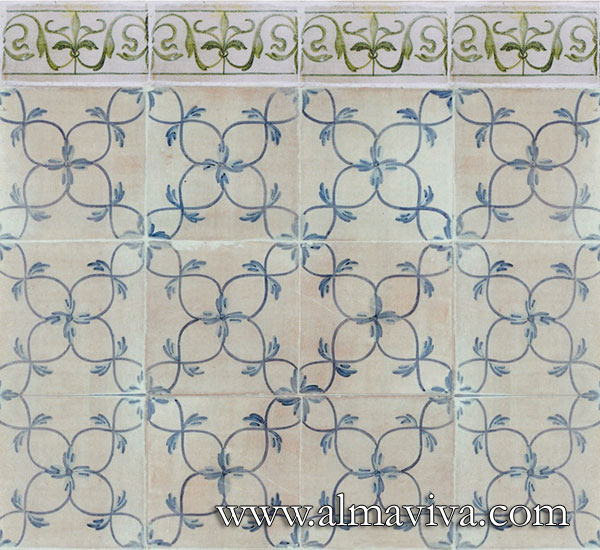
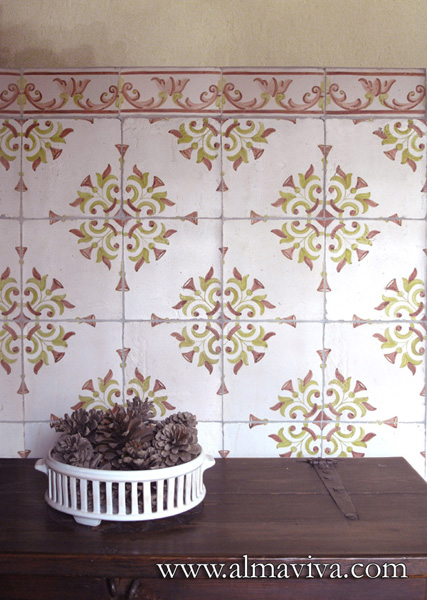
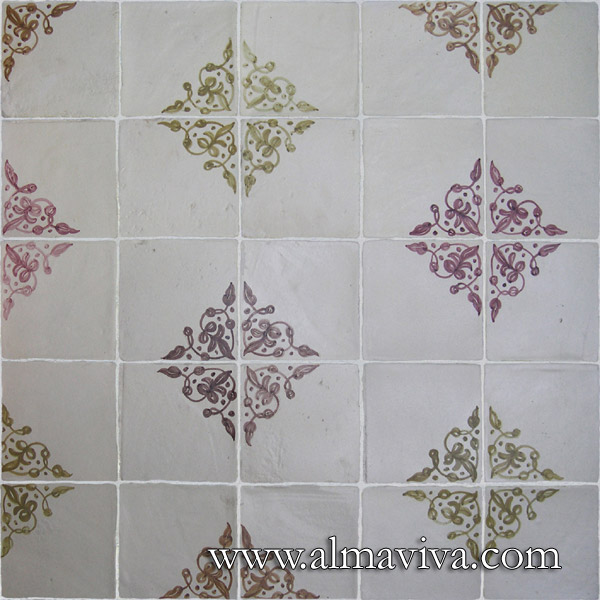
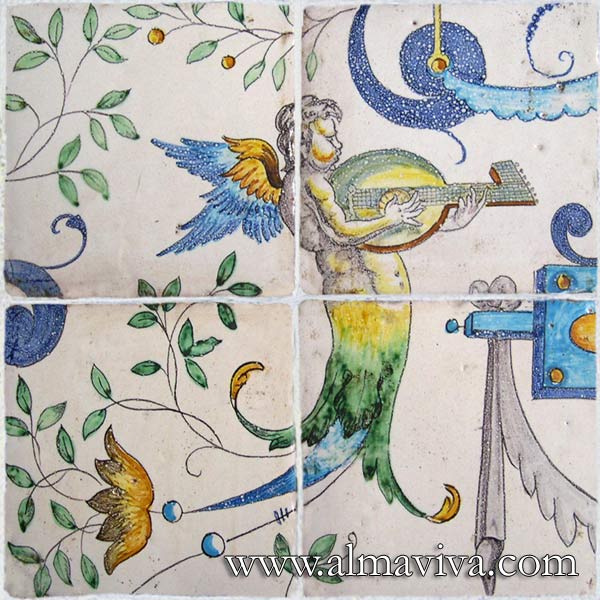
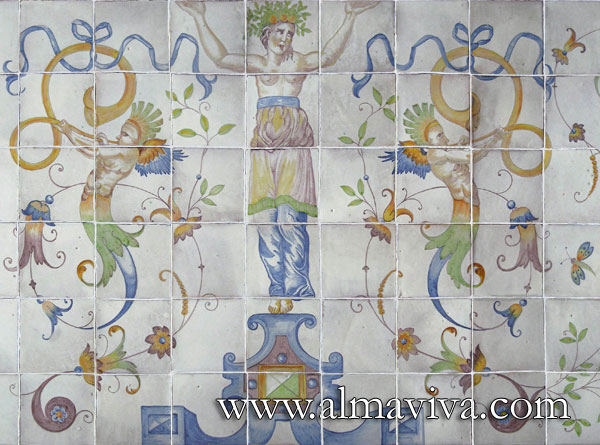
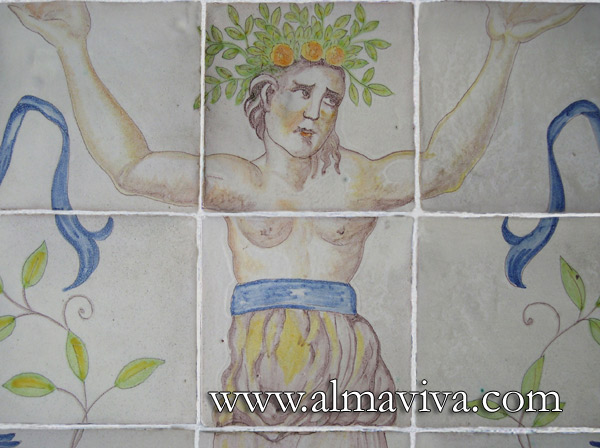
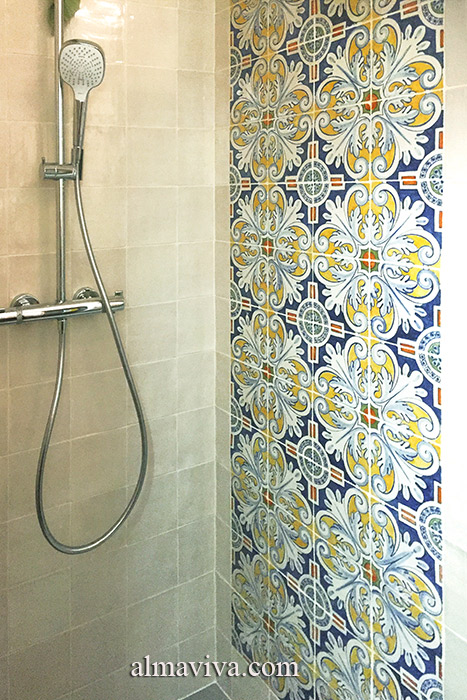
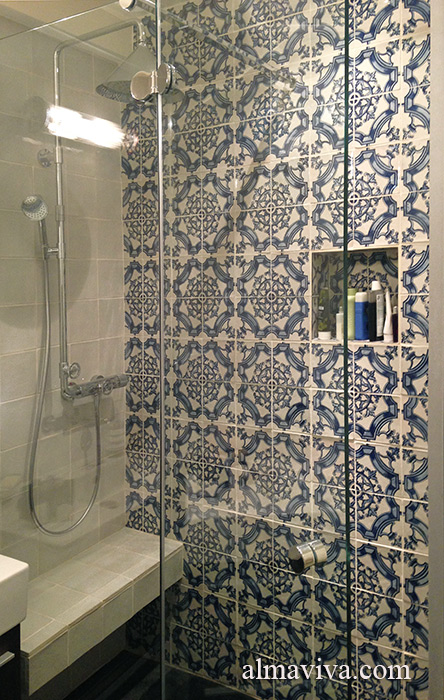
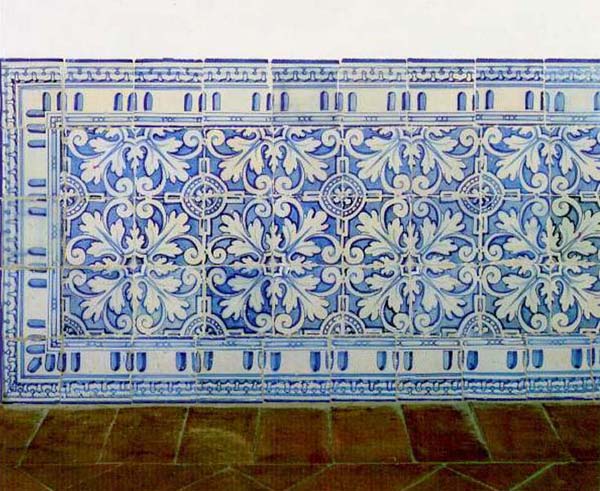
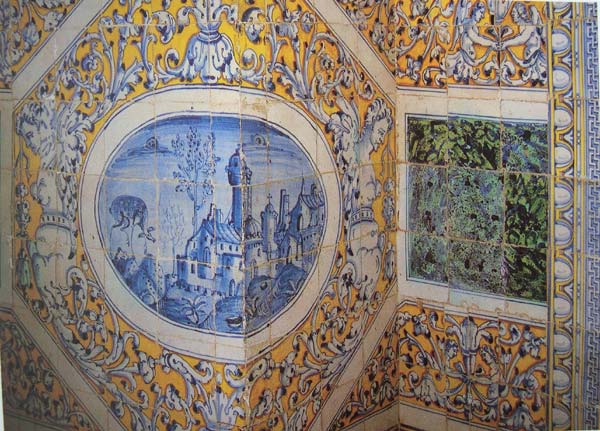
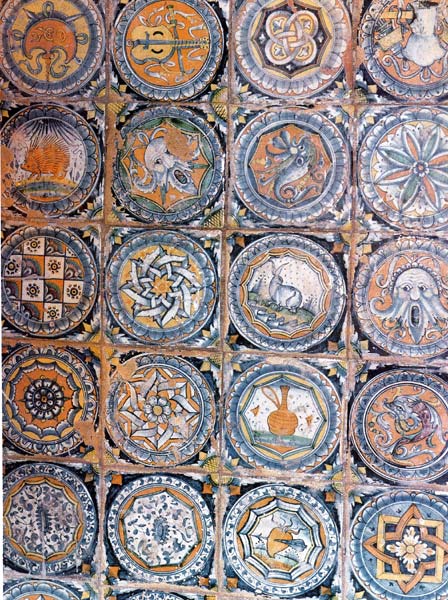
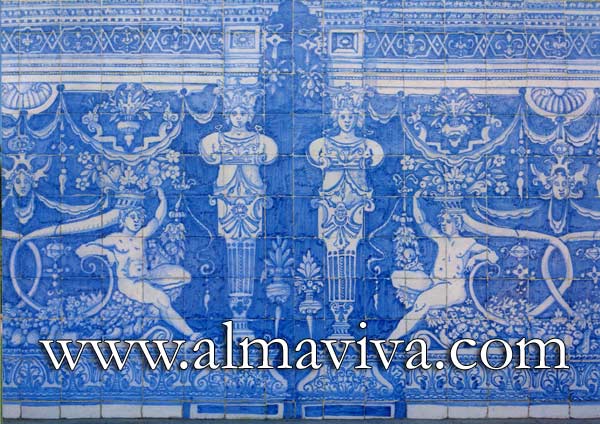
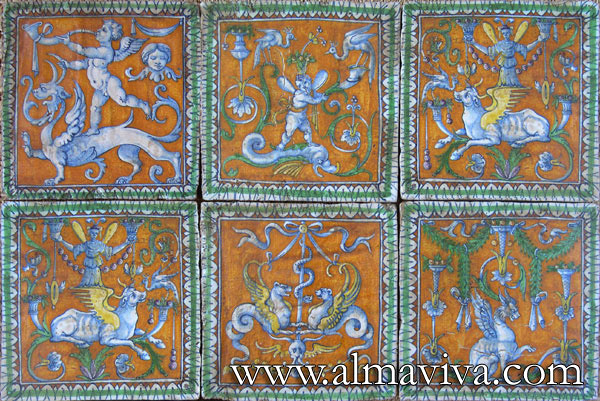
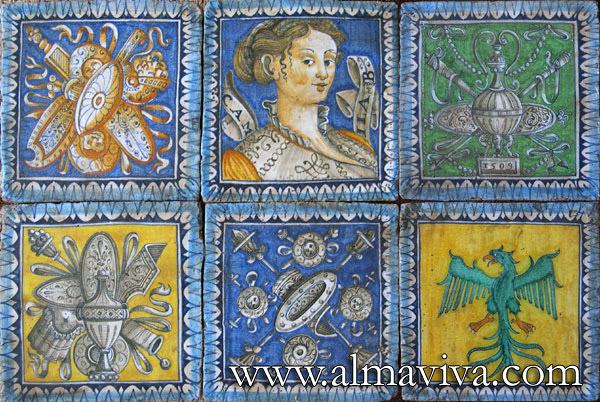
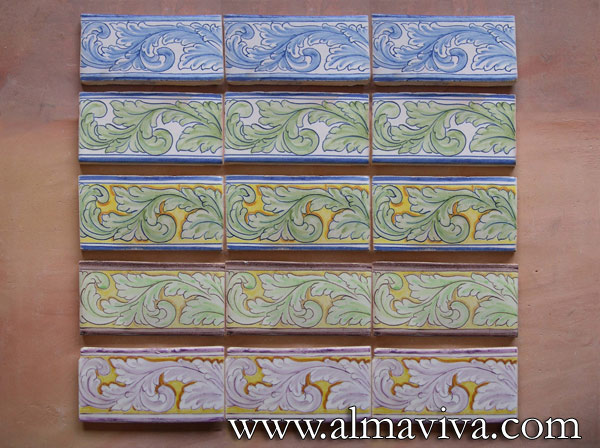
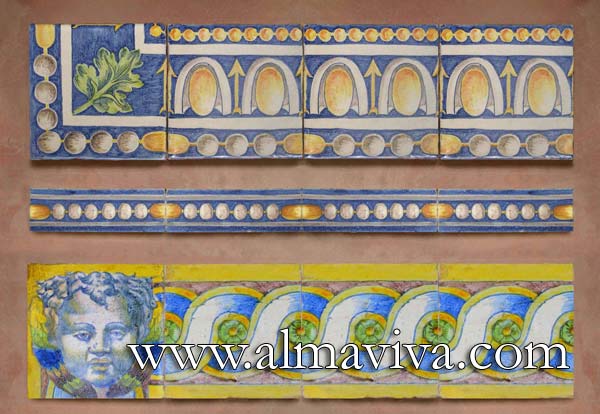
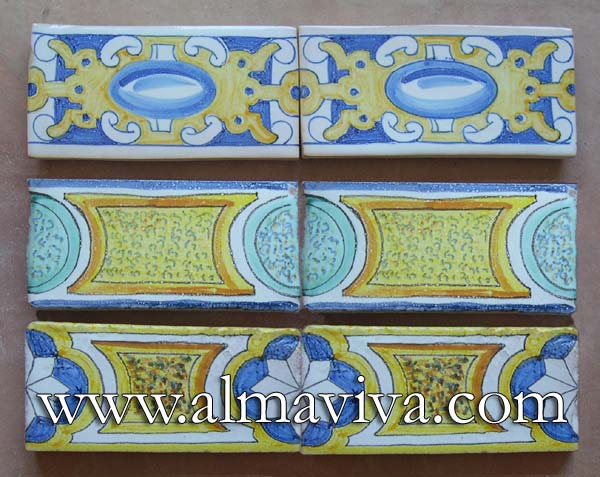
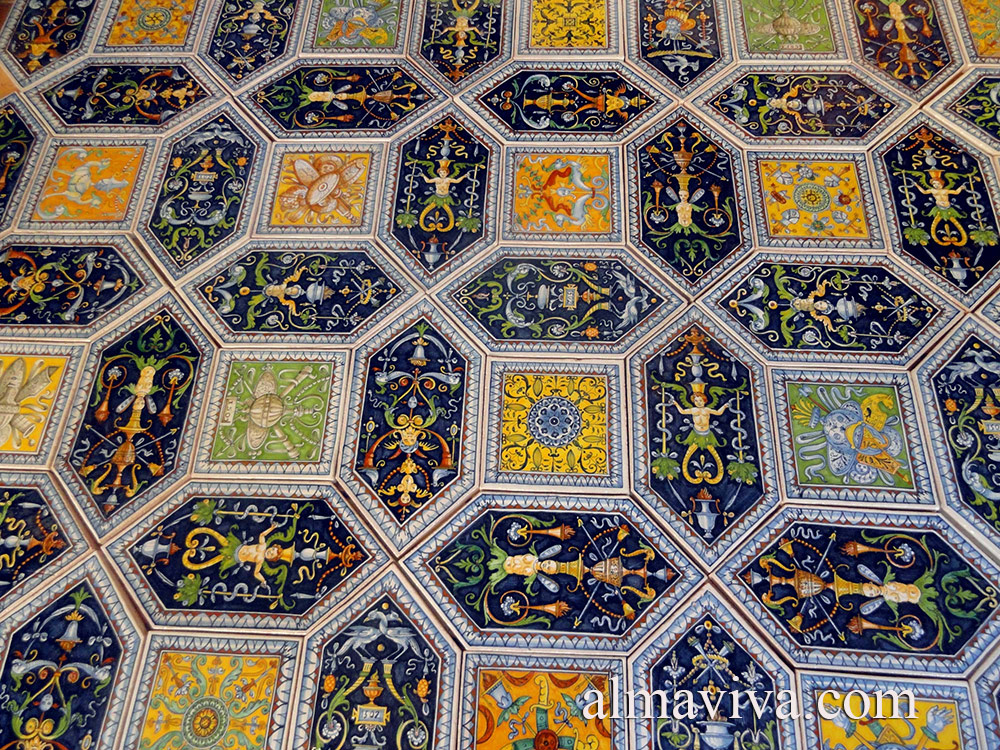
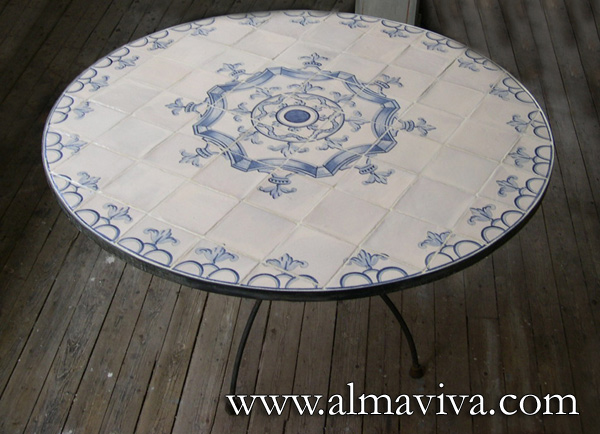
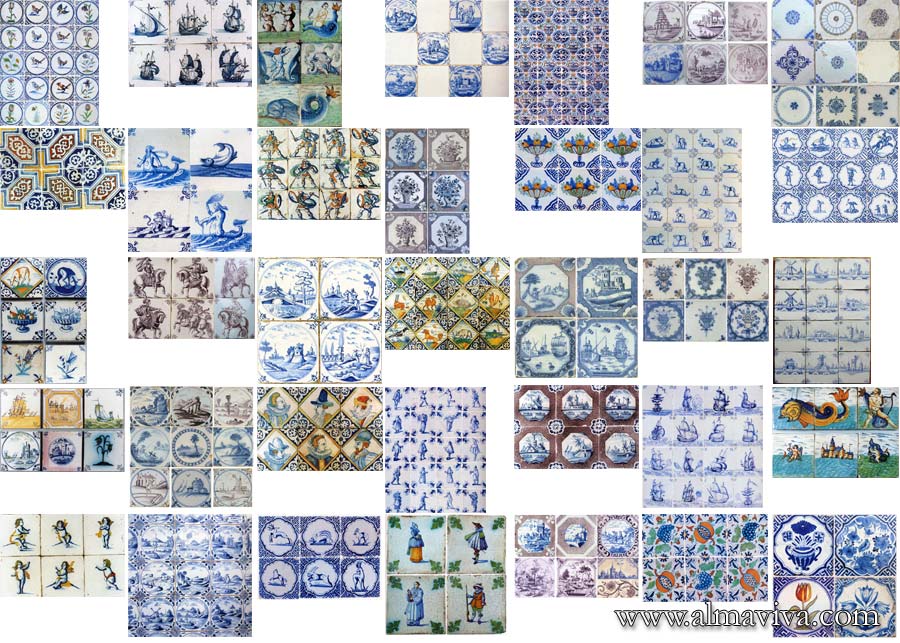
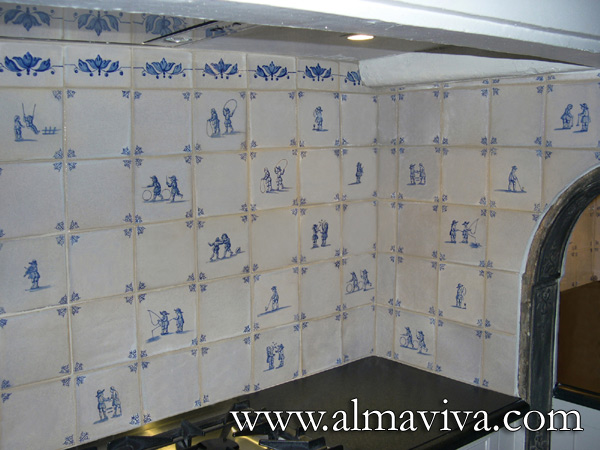
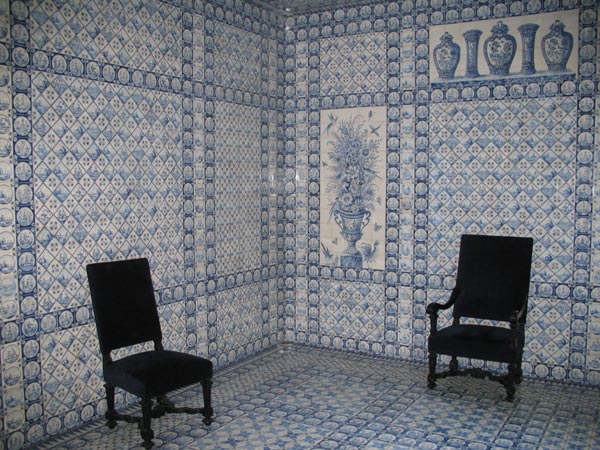
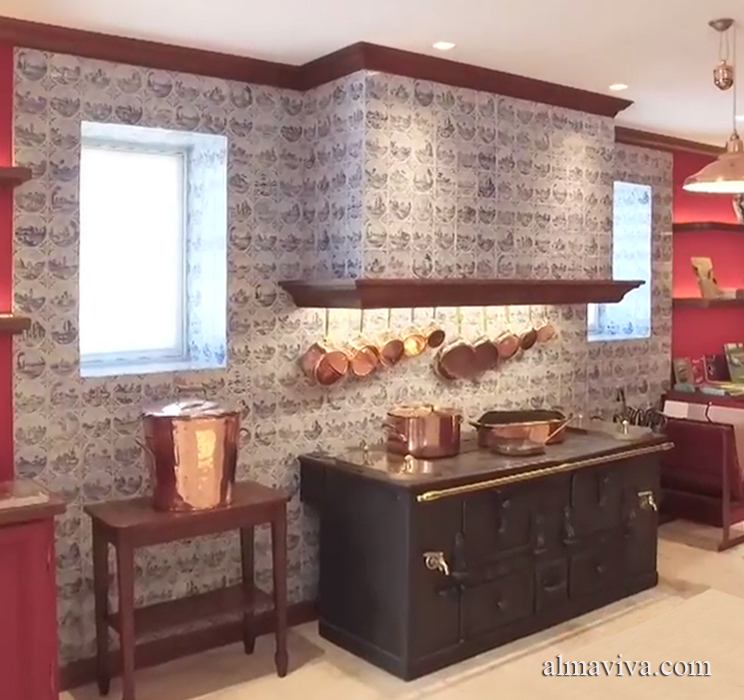
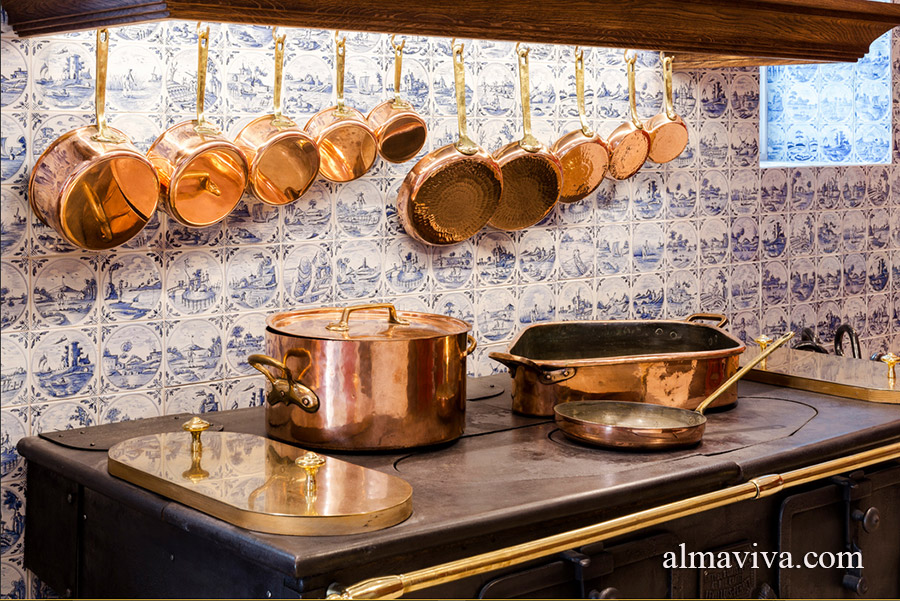
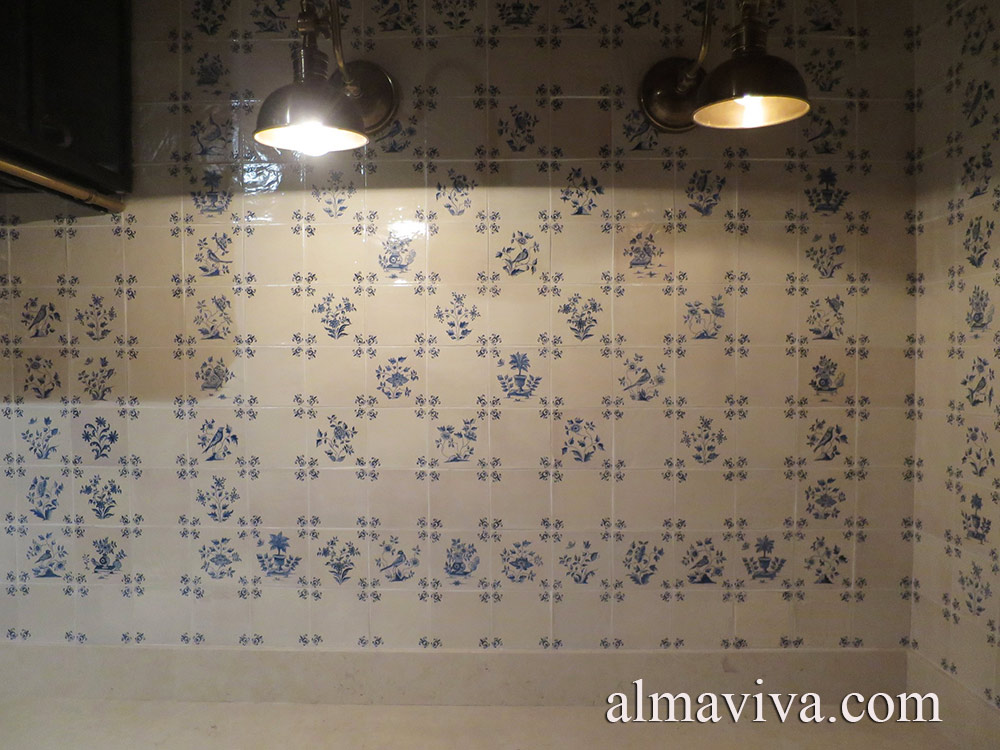
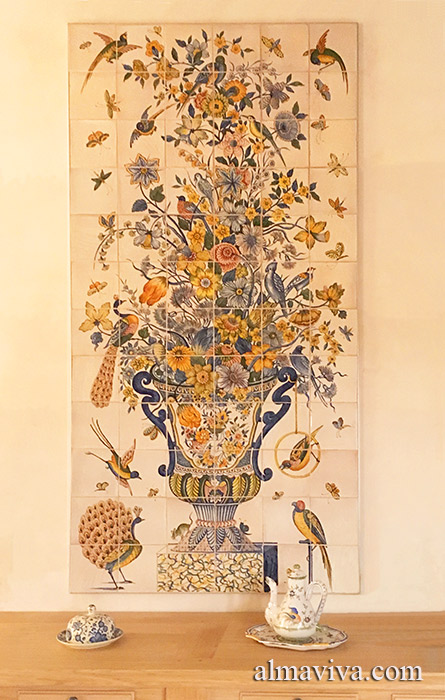
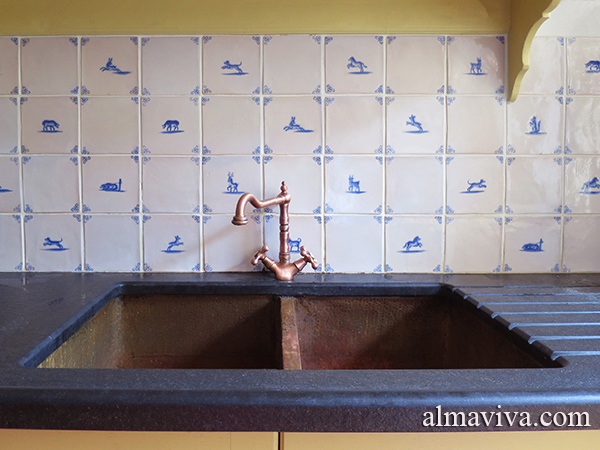
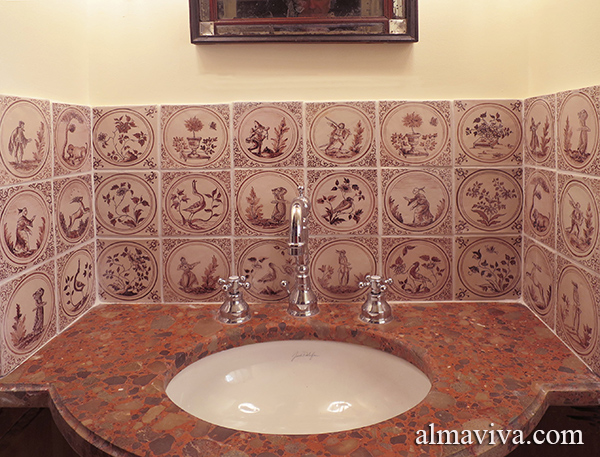
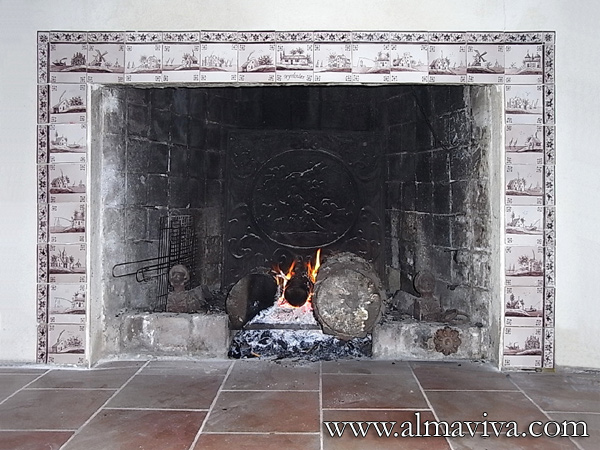
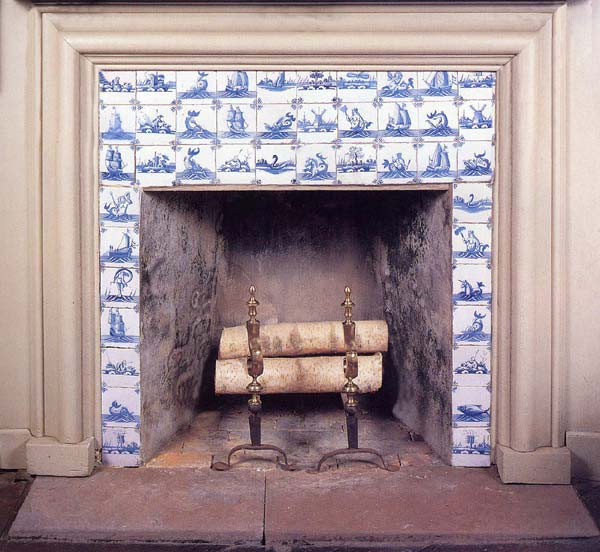
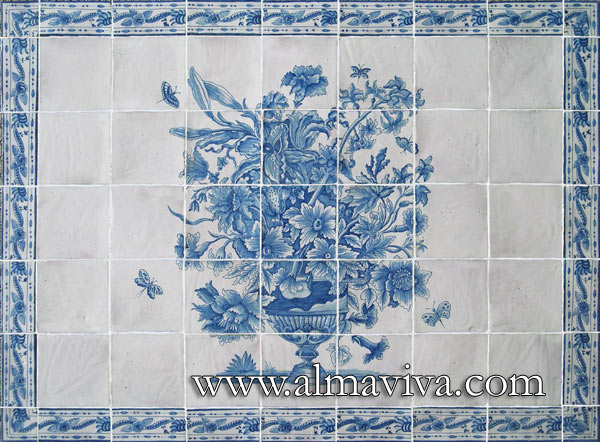
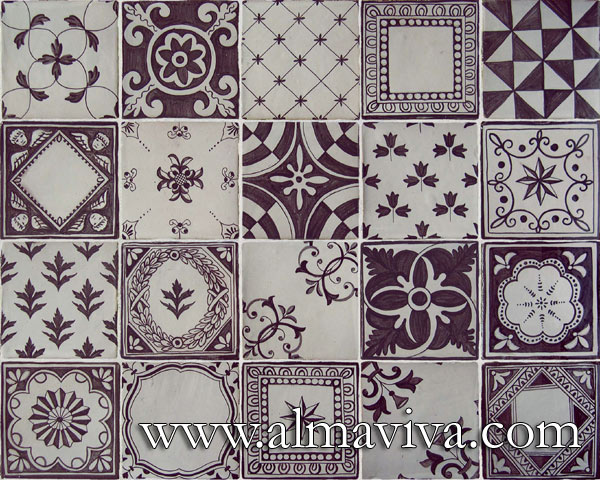
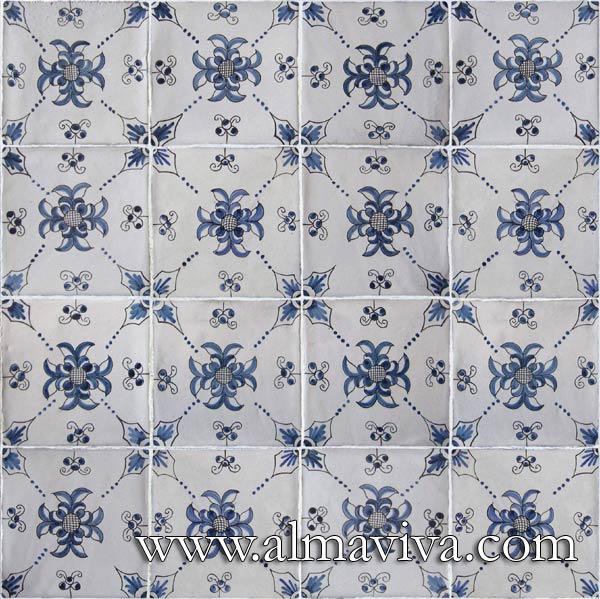
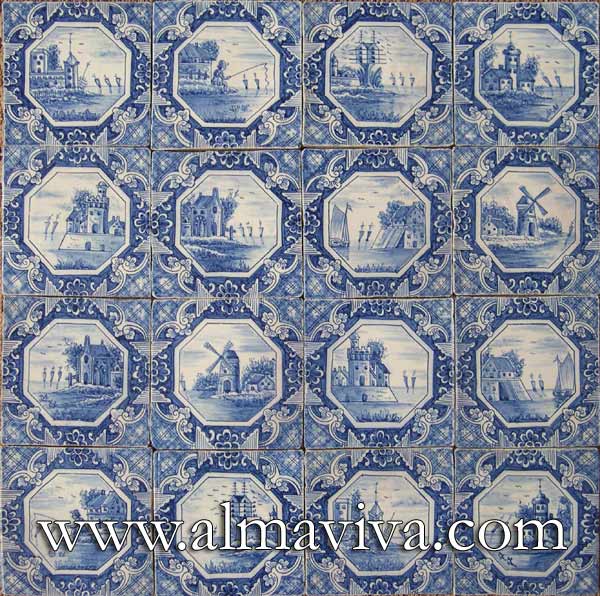
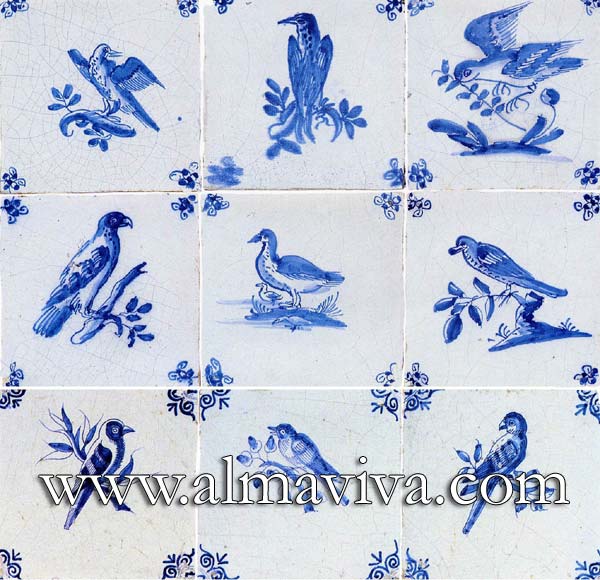
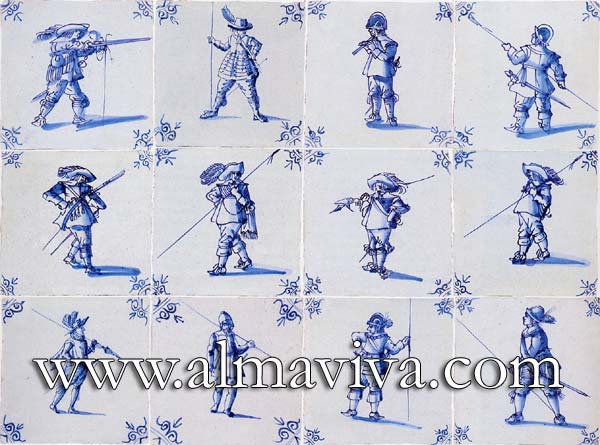
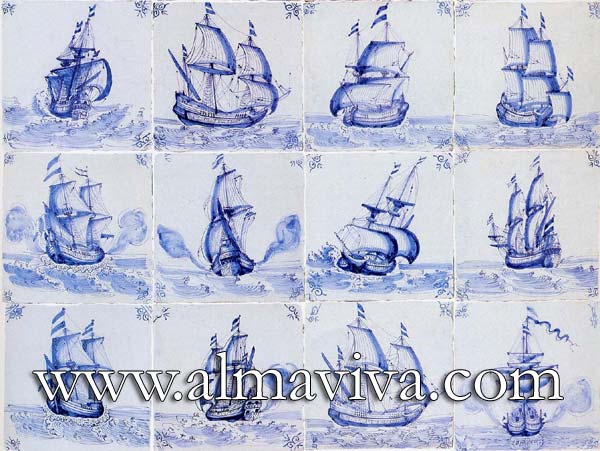
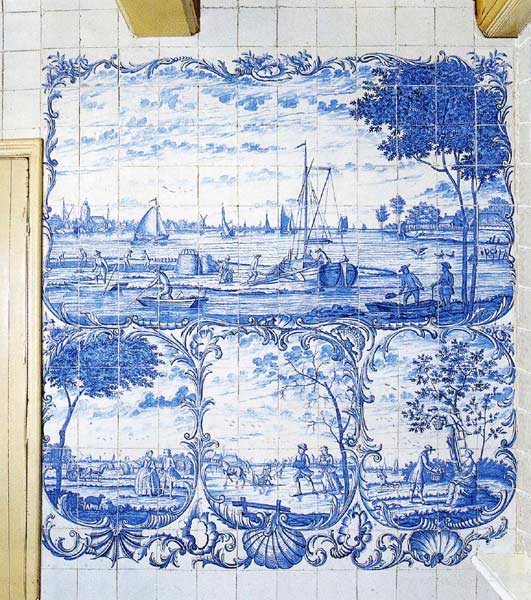
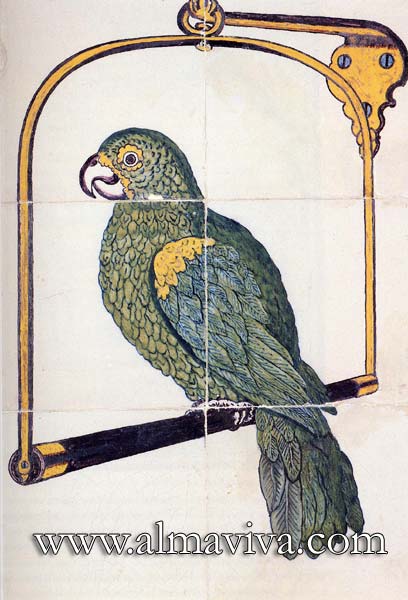
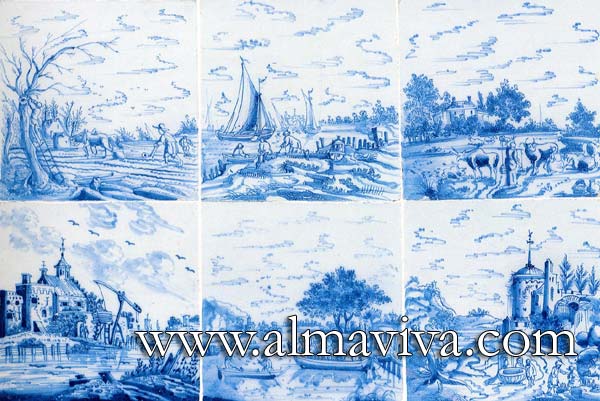
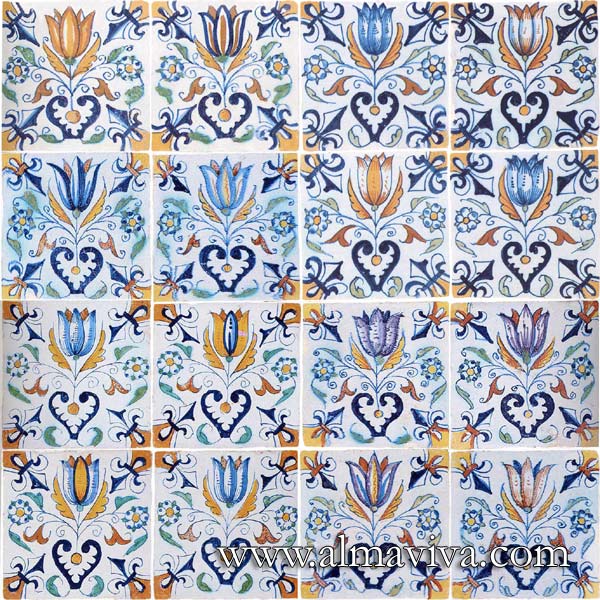
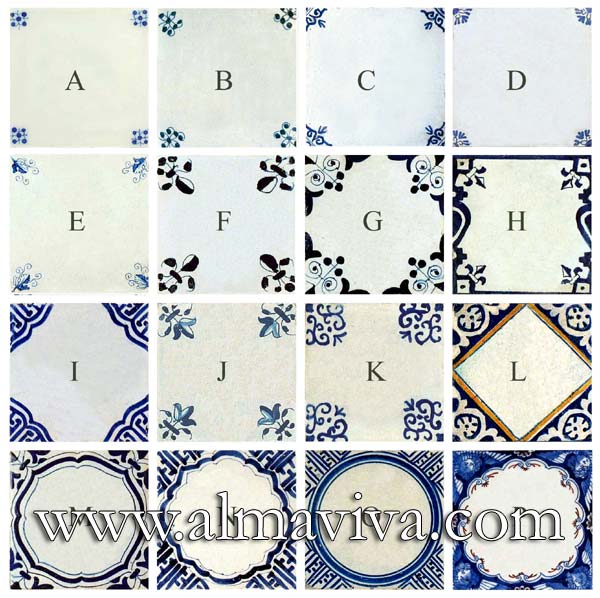
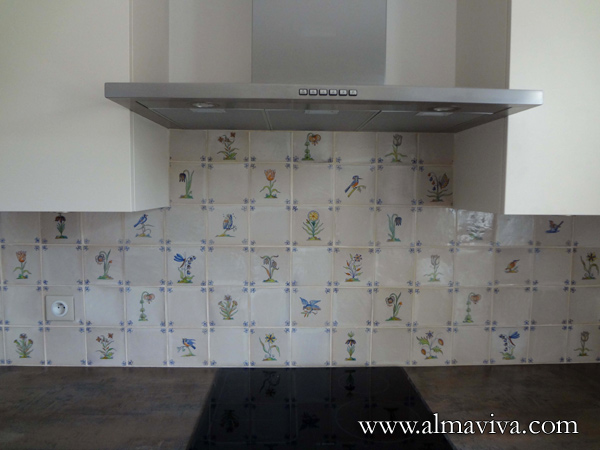
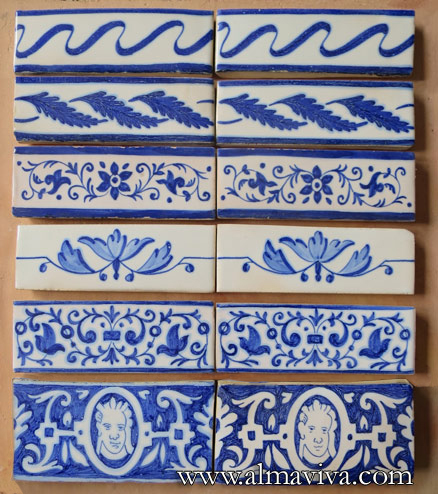
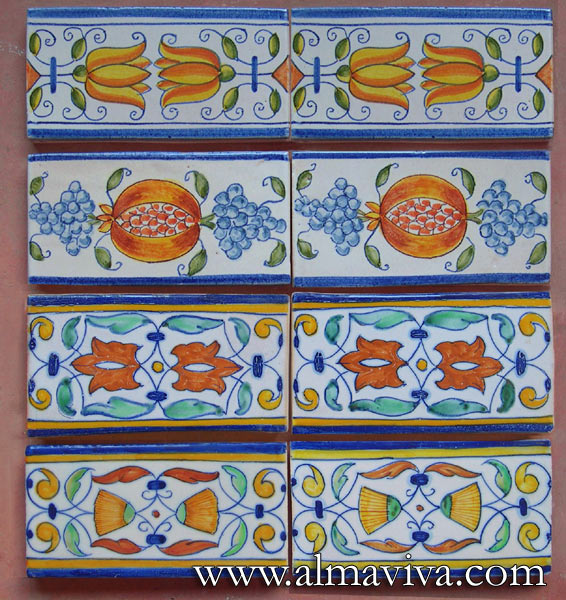
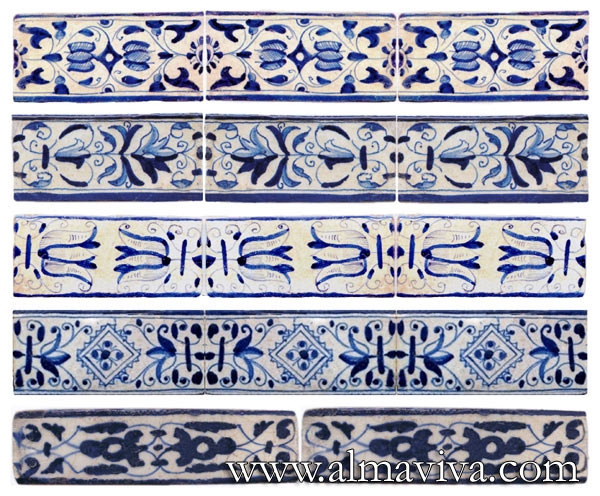
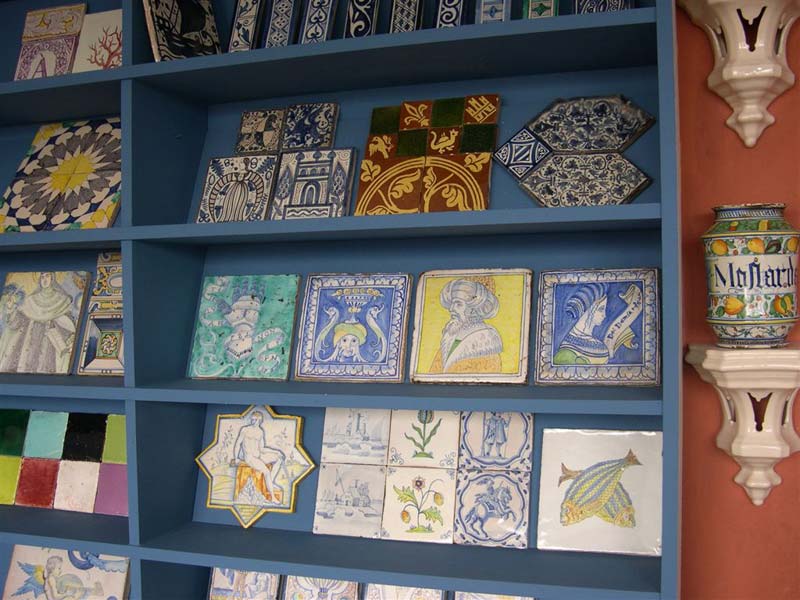
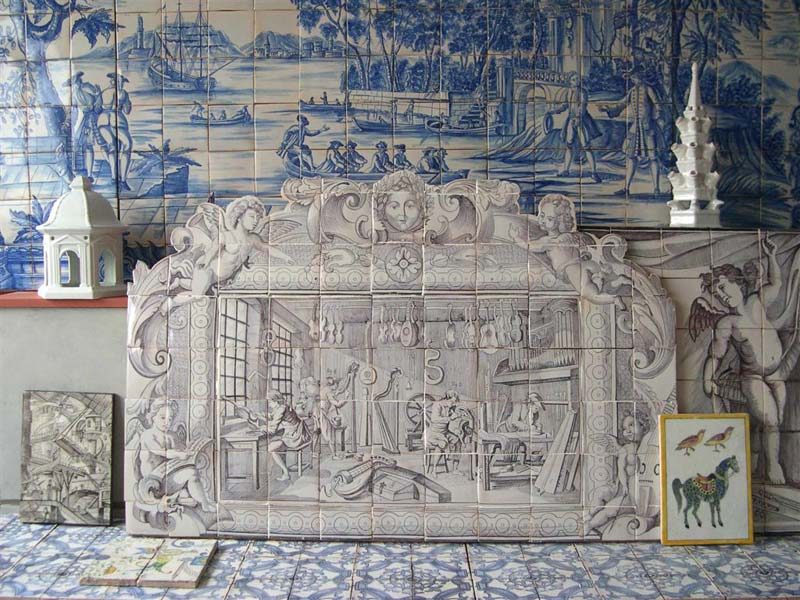
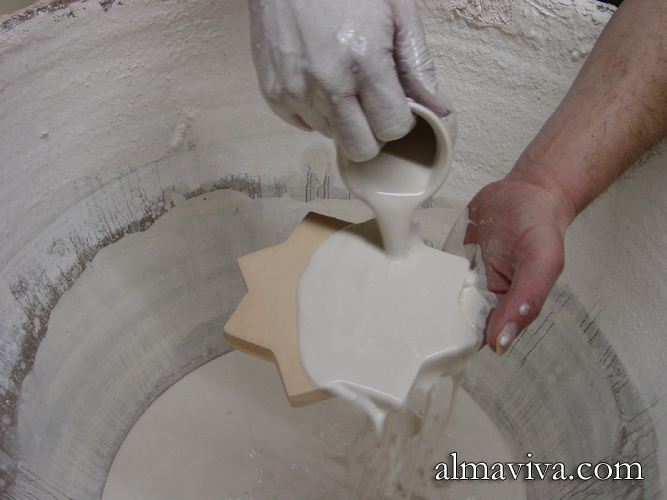
Backsplash, countertop, tile flooring: various contemporary examples
-

-
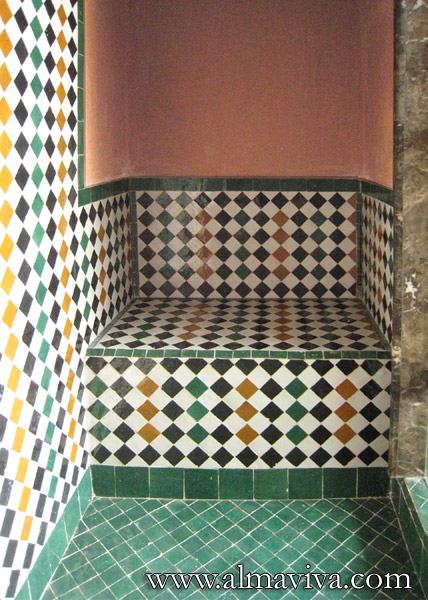
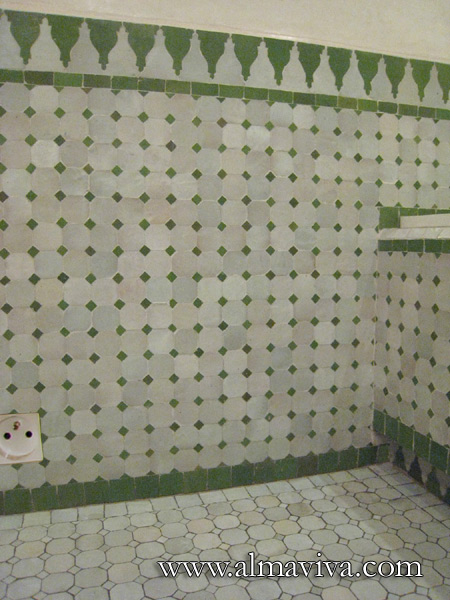
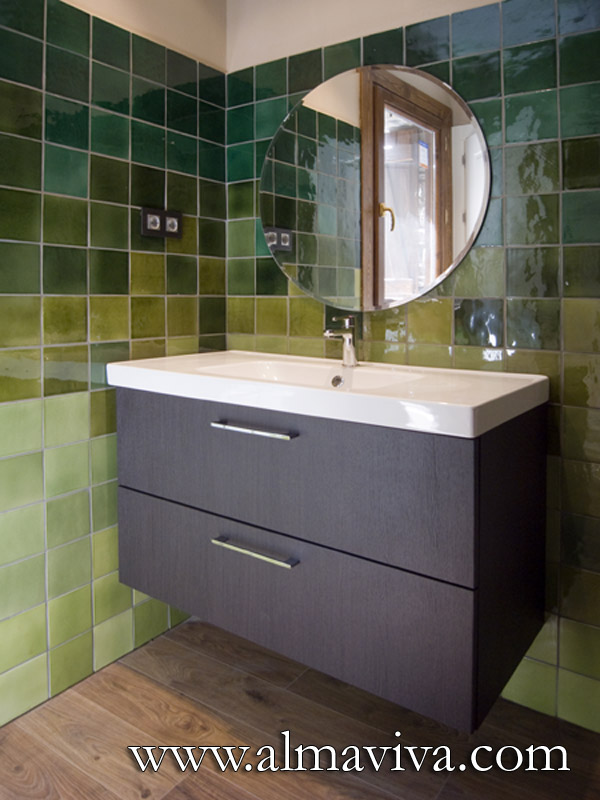
Ref. CD30 - Bathroom decorated with handmade tiles in shades of green
-
View Picture
-

-
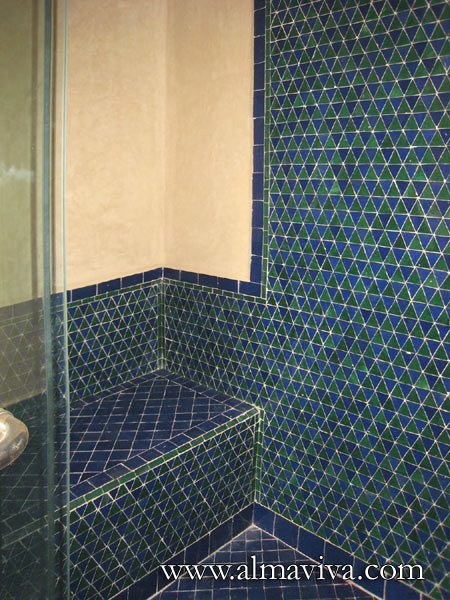
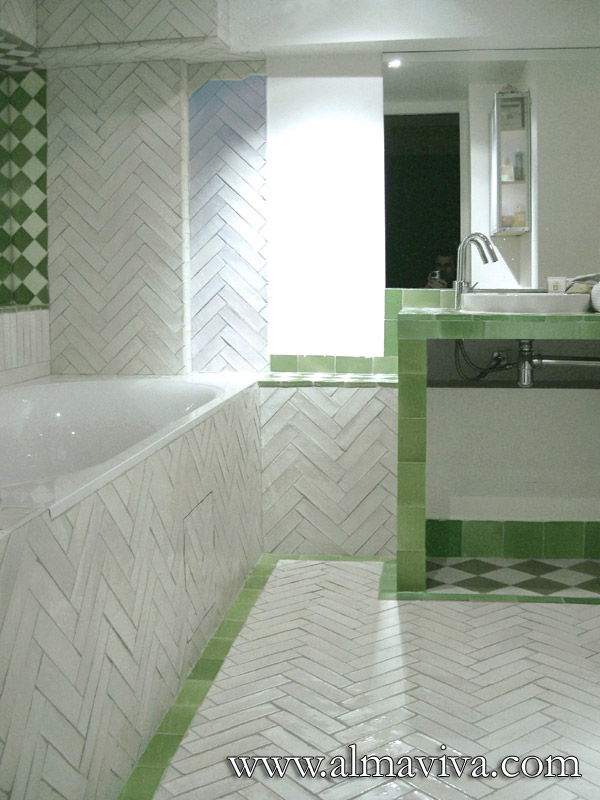
Ref. CD31 - Zellige in a bathroom. Moroccan stylen tiles
-
View Picture
-

-
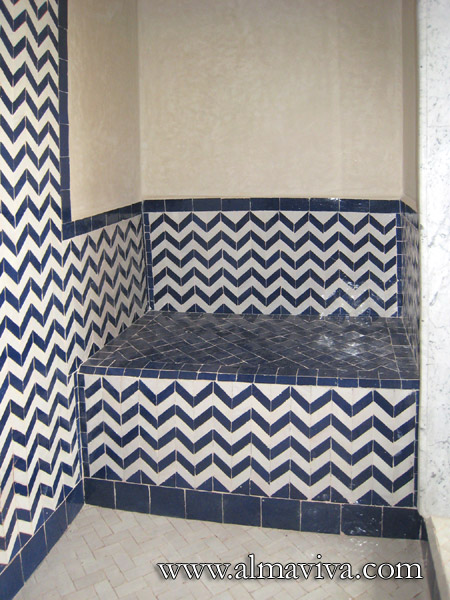
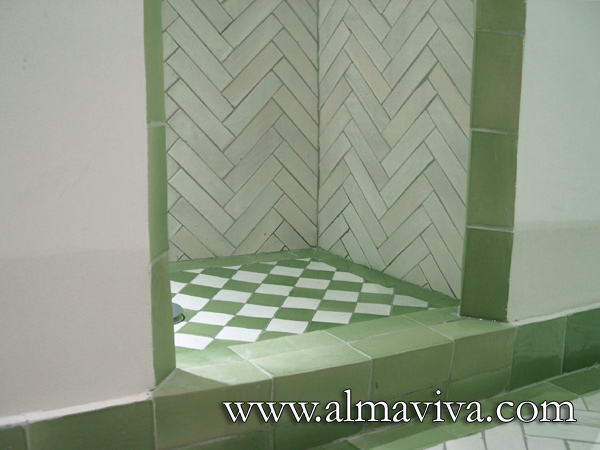
Ref. CD32 - Zellige in a bathroom. Moroccan style tiles
-
View Picture
-

-
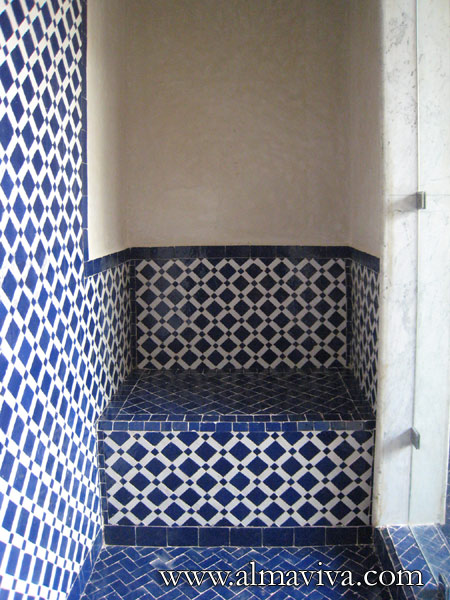
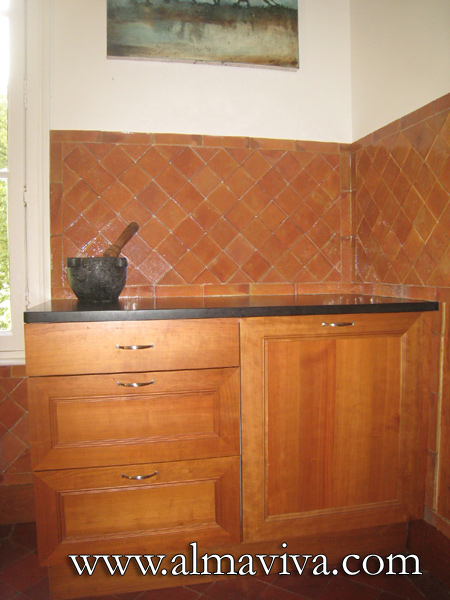
Ref. CD42 - Terracotta handmade tiles for kitchen
-
View Picture
-

-
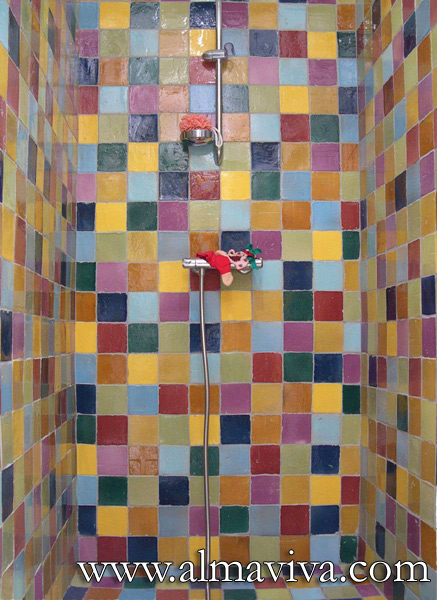
Ref. CD28 - Many-coloured shower. Plain tiles 10x10 cm (about 4''x4''), shiny glaze, various colours
-
View Picture
-

-
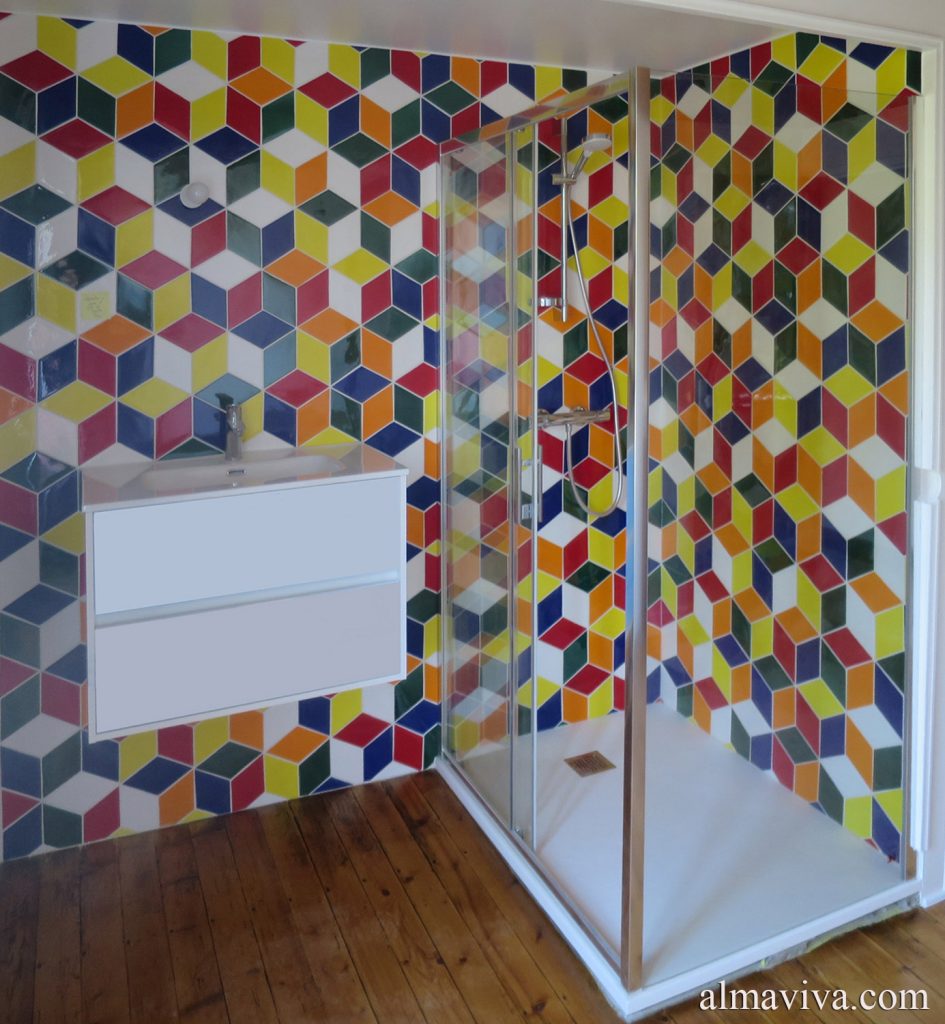
Ref. CD43 - Another coloured shower, inspired by the Rubik's cube
-
View Picture
-

-
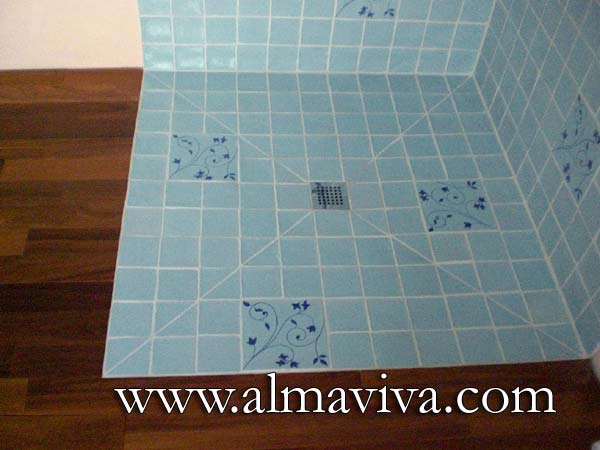
Ref. CD23 - Celadon bathroom (see Keywords). 10x10 cm (about 4''x4'') plain tiles in the shower, alternating with a 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'') decorated tile
-
View Picture
-

-
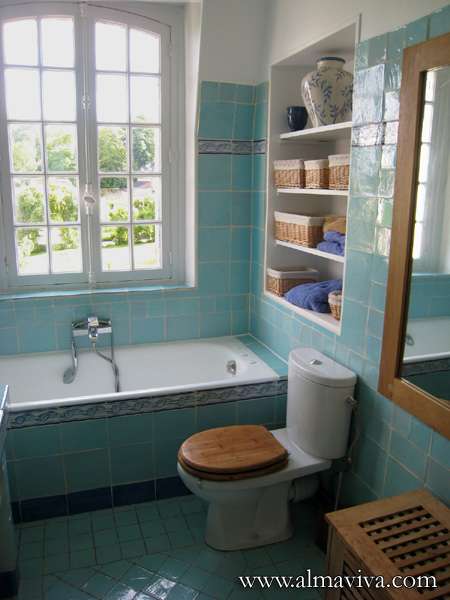
Ref. CD36 - Turquoise bathroom. Decor alterning 20x20 cm tiles (about 8''x8''), 10x10 cm tiles (about 4''x4''), and a frieze
-
View Picture
-

-
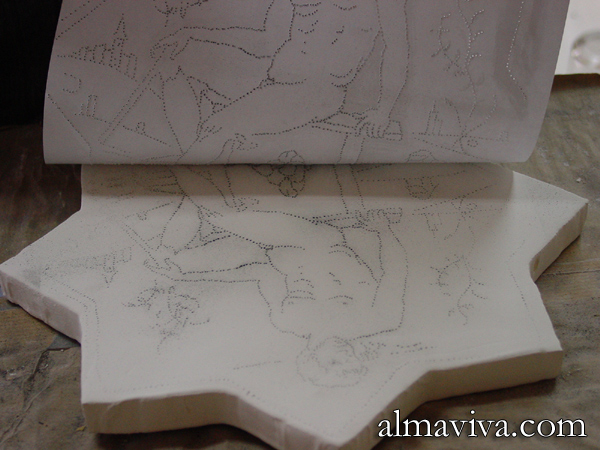
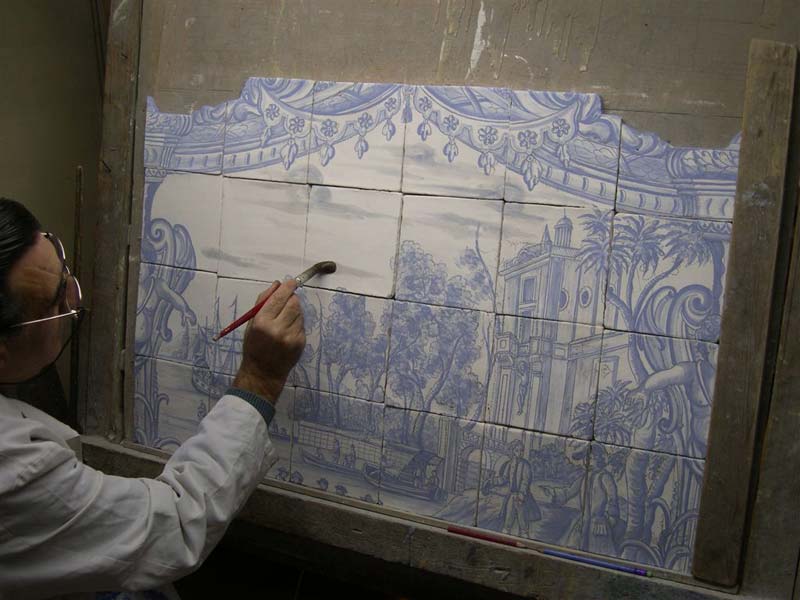
Ref. CD53 - Singerie inspired by Jean-Baptiste Huet painted in the manner of azulejos: the painter and his model
-
View Picture
-

-
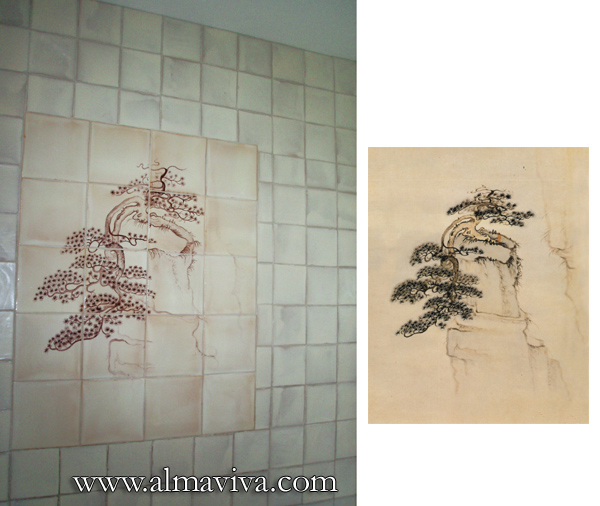
Ref. CD15 - Tree on Mont Huang. Dim 80x100 cm (about 31,5'x3,3'). Aside, the pattern that inspired this tile panel
-
View Picture
-

-
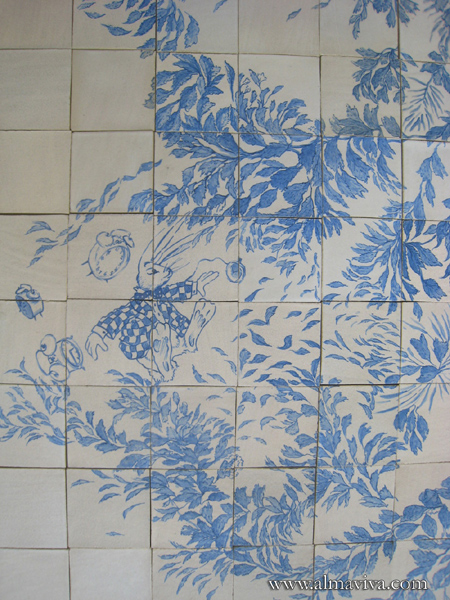
Ref. CD21 - Floor handmade tiles inspired from Alice in Wonderland
-
View Picture
-

-
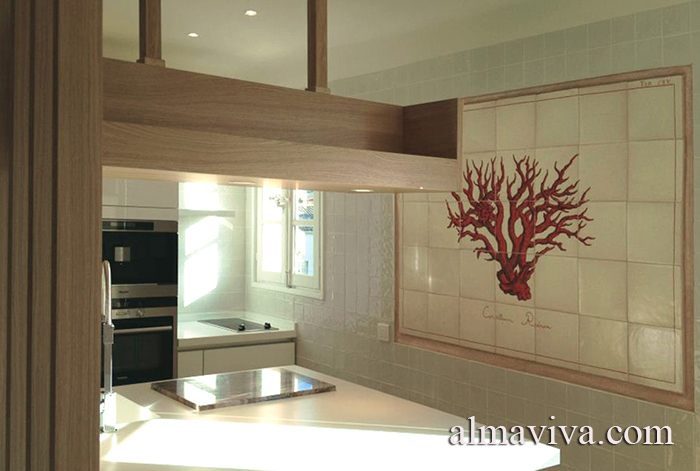
Ref. CD49 - Coral painted on a ceramic panel
-
View Picture
-

-
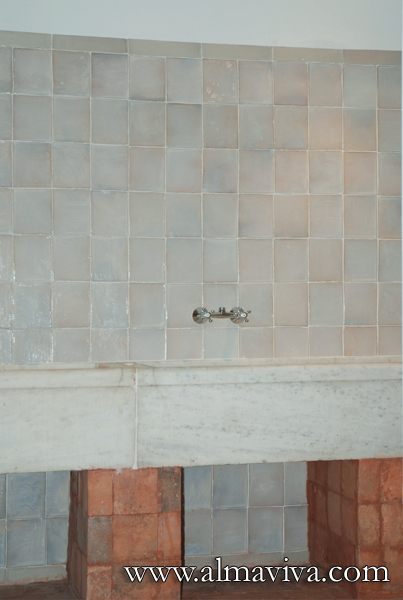
Ref. CD27 - Tiles 10x7 cm (about 4''x3'') glazed with different whites to give a rich variety of tones and reflections
-
View Picture
-

-
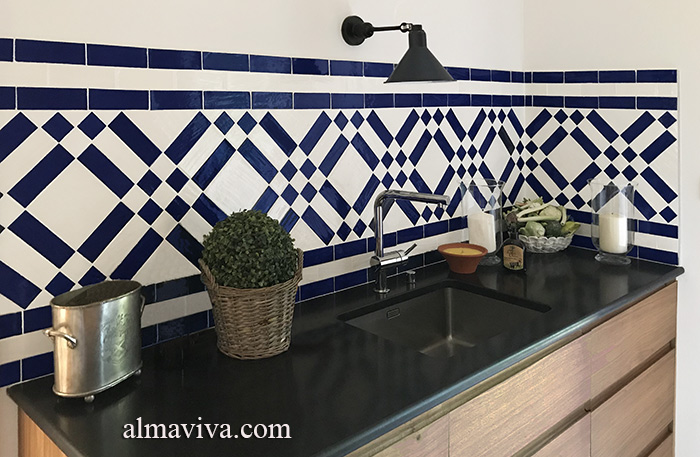
Ref. CD52 - White and blue checkered kitchen credenza
-
View Picture
-

-
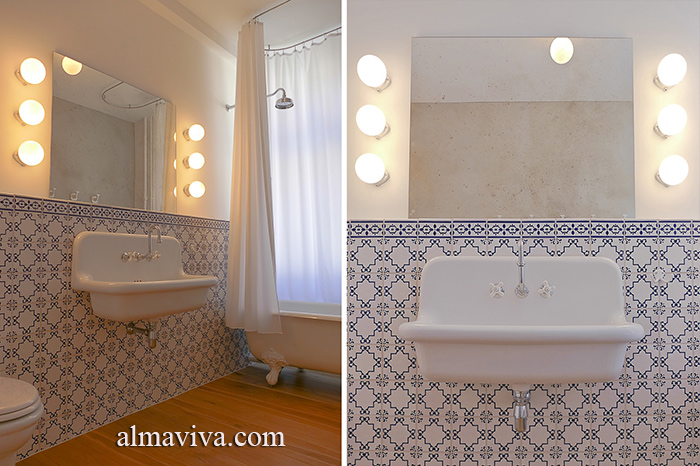
Ref. CD48 - Tiles with geometric patterns painted with stencil
-
View Picture
-

-
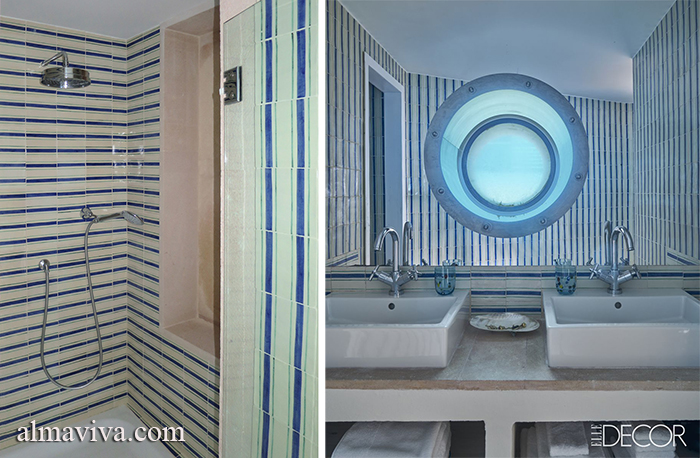
Ref. CD51 - Bathroom tiles with stripes
-
View Picture
-

-
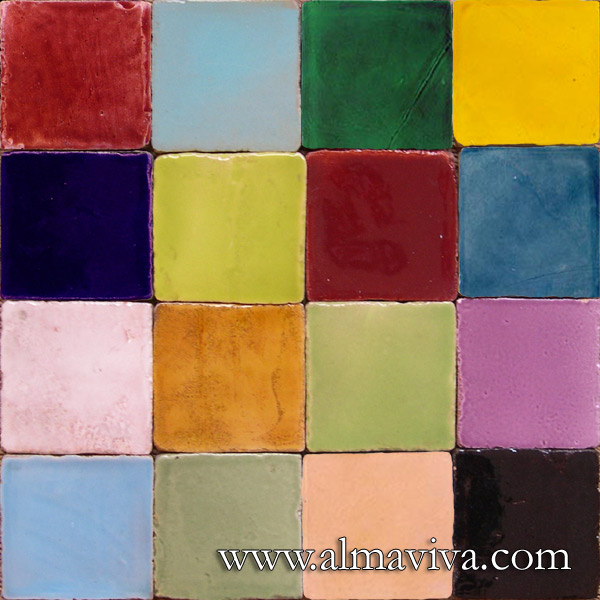
Ref. CD10 - Matt plain tiles in shades of blue
-
View Picture
-

-
Ref. CD09 - Shiny glazes. Tiles 10x10, or 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 4''x4'', 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
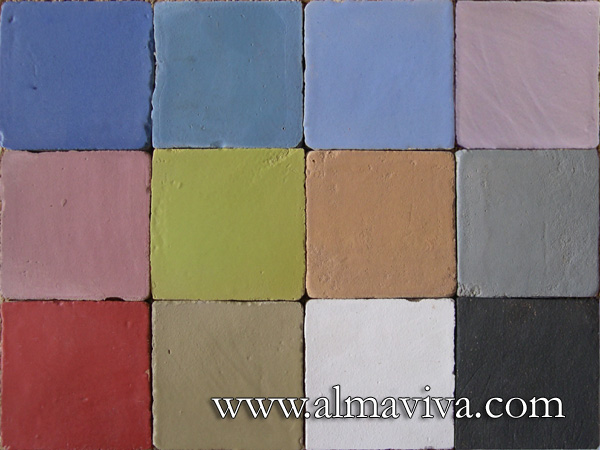
Ref. CD18 - Matt glazes. Tiles 10x10, or 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 4''x4'', 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
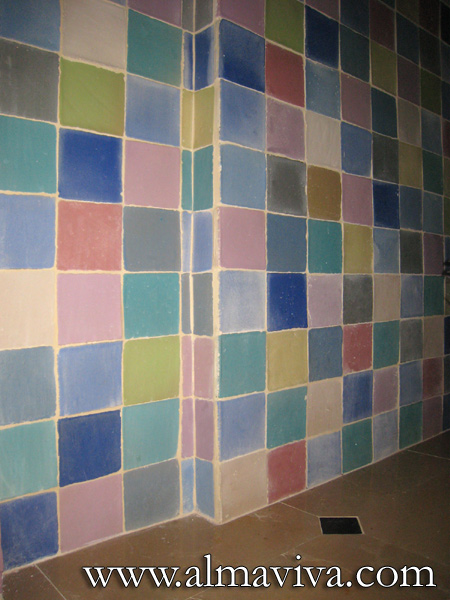
Ref. CD04 - Many-coloured wall tiles. 10x10 cm (about 4''x4''), unpolished glazes of different colours
-
View Picture
-

-
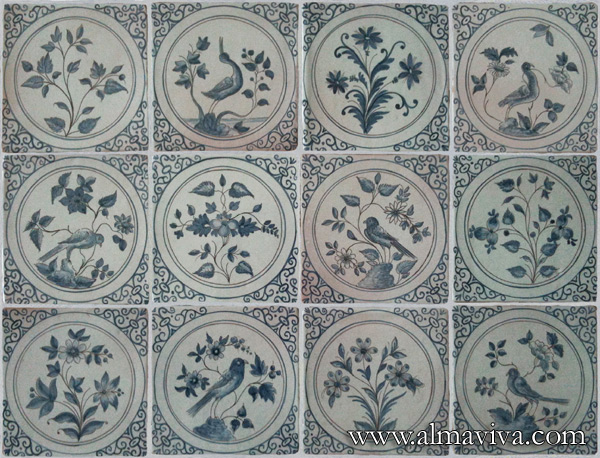
Ref. CD11 - Bulb flowers. Each flower measures 15x30 cm (about 6''x12''). Collection of 12 different flowers, created by Almaviva
-
View Picture
-

-
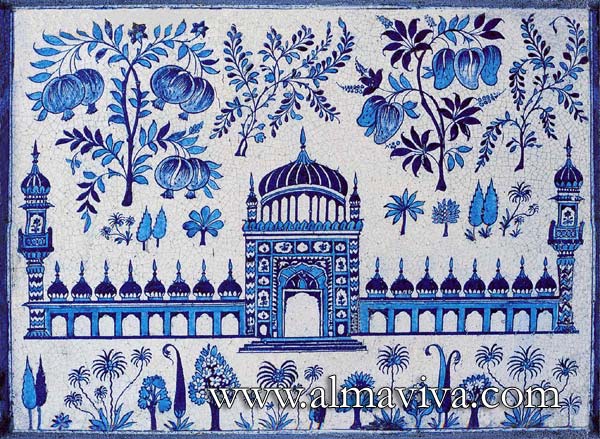
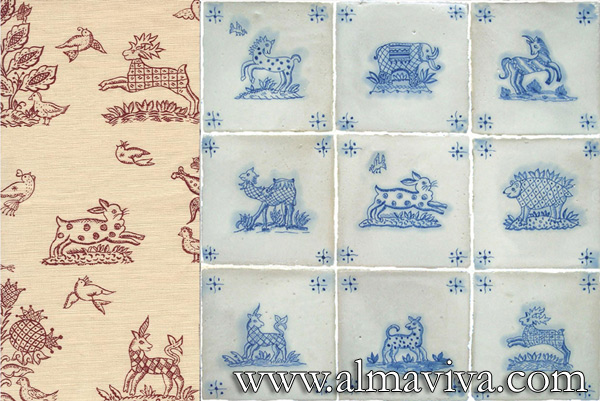
Ref. CD22 - Indian Collection. Patterns inspired from an indian fabric, tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
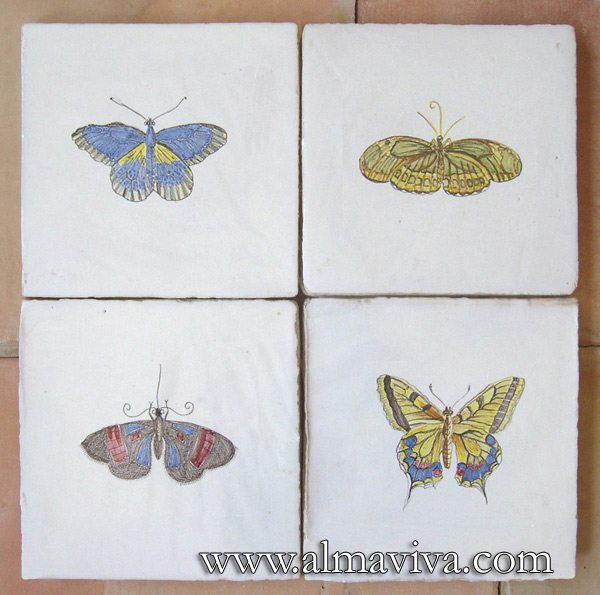
Ref. CD07 - Butterflies. Tiles 20x20 or 15x15 cm (about 8''x8'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
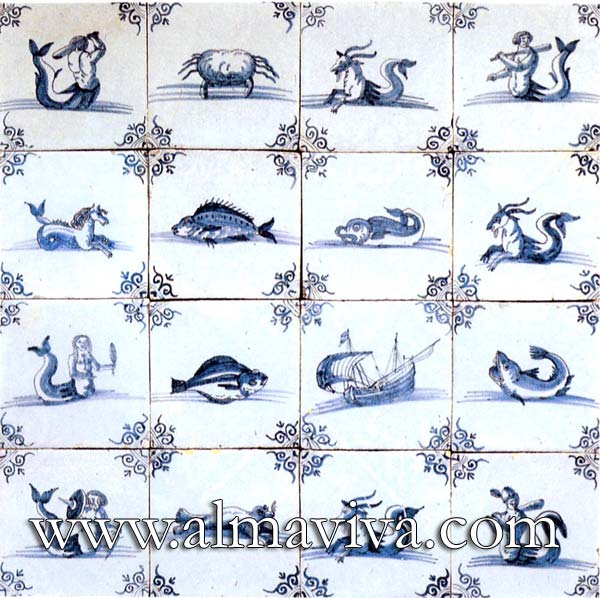
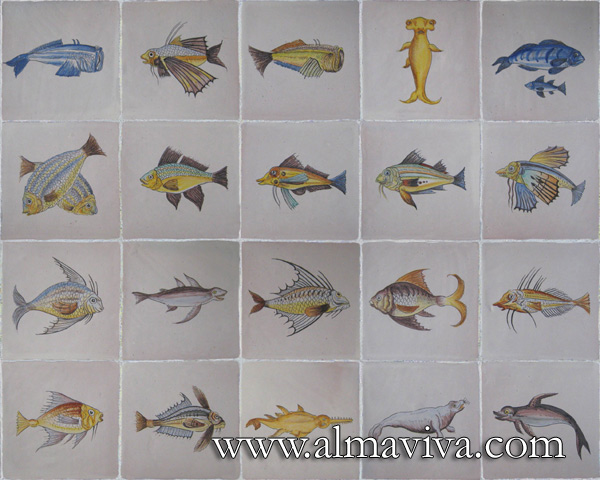
Ref. CD29 - Fish. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-

-
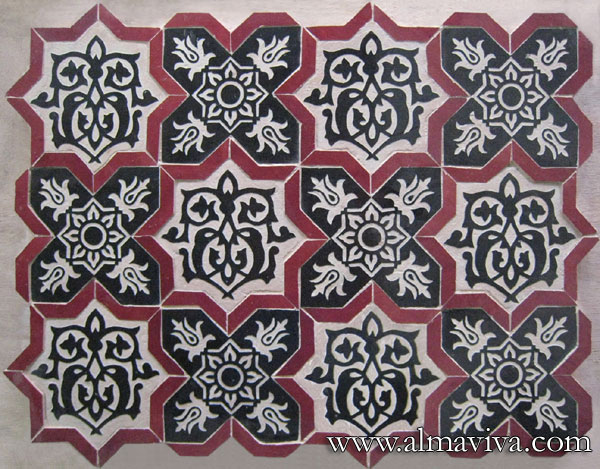
Ref. CD41 - Interlace 4 different colours. Tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
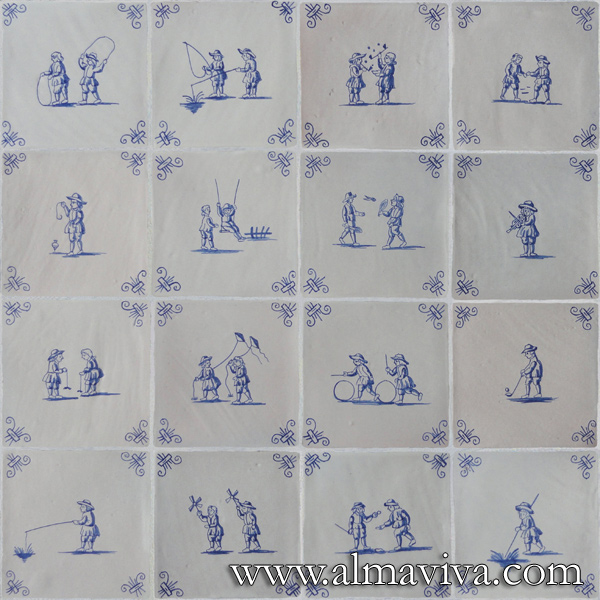
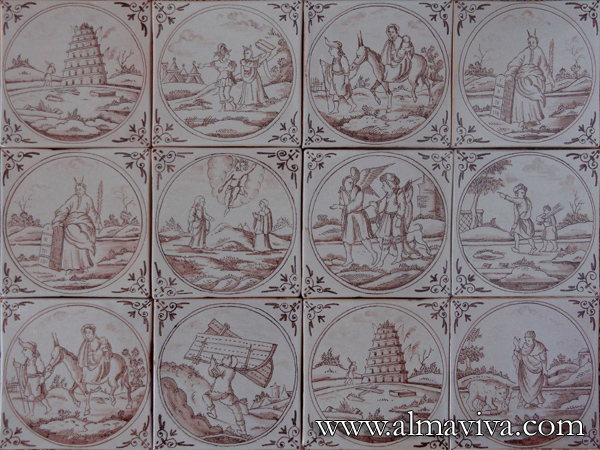
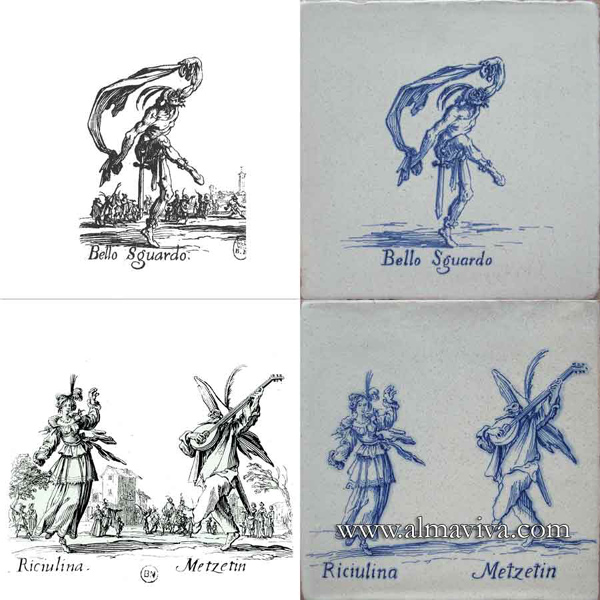
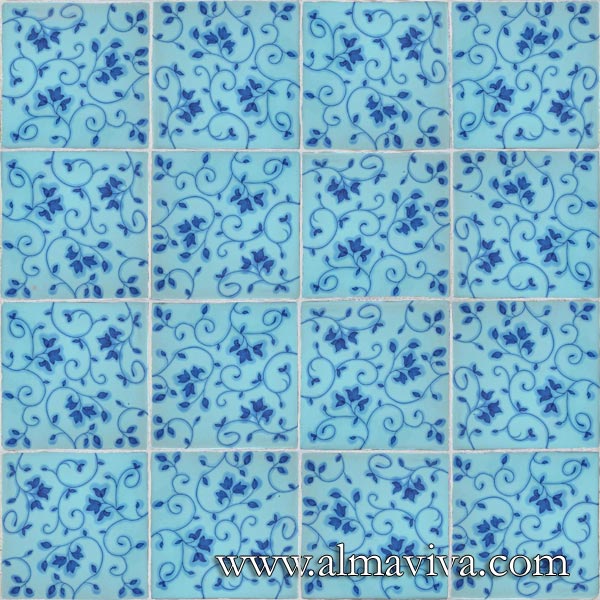
Ref. CD19 - Commedia Dell'Arte Characters. Tiles 20 x 20 cm (about 8''x8''). Reproduction of 17th c. engravings (see archives)
-
View Picture
-
-
Ref. CD24 - Celadon Interlace (see keywords). Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-

-
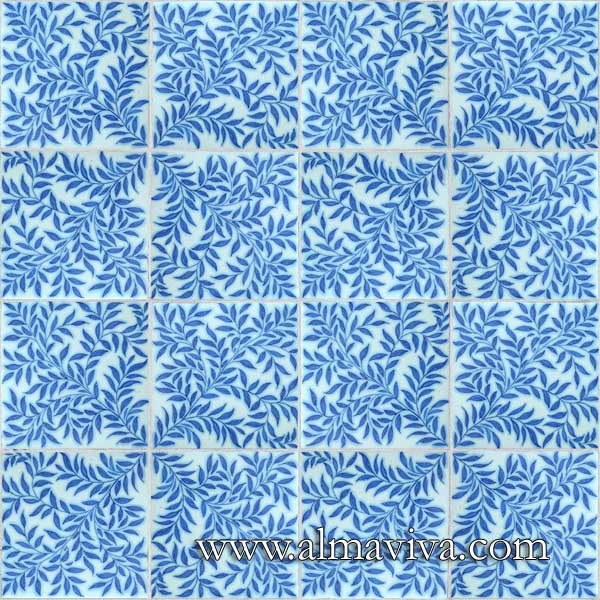
Ref. CD33 - Leaves. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
-
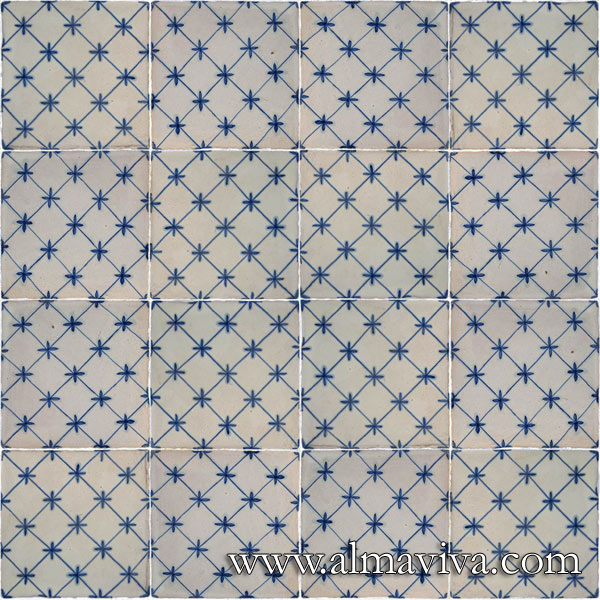
Ref. CD45 - Blue square pattern. Tiles 10x10, 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 4''x4'', 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
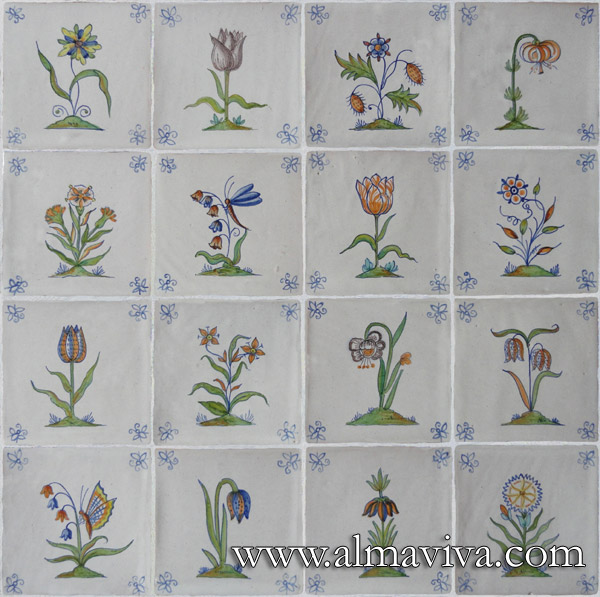
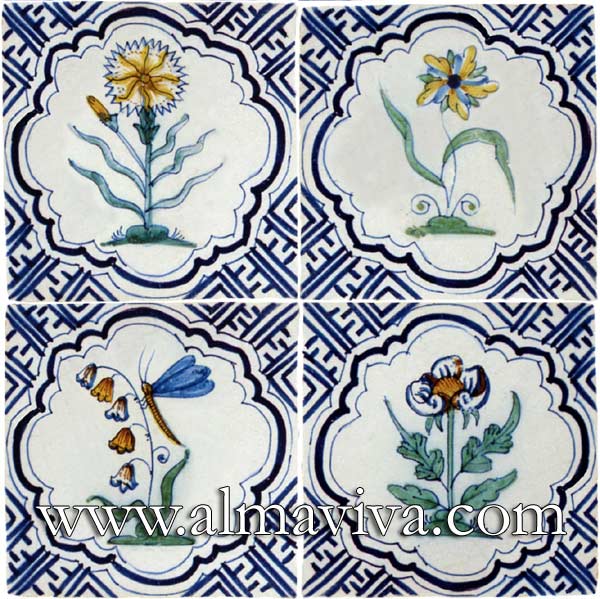
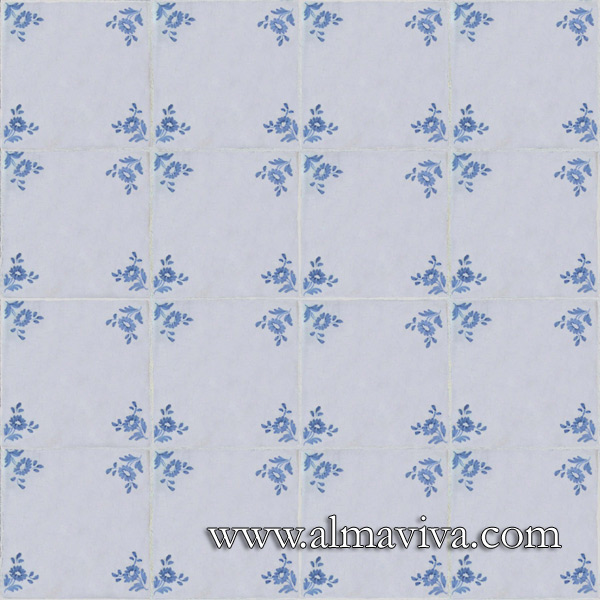
Ref. CD17 - Flowers tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
Ref. CD17b - Tiles with corner ''flower'', 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
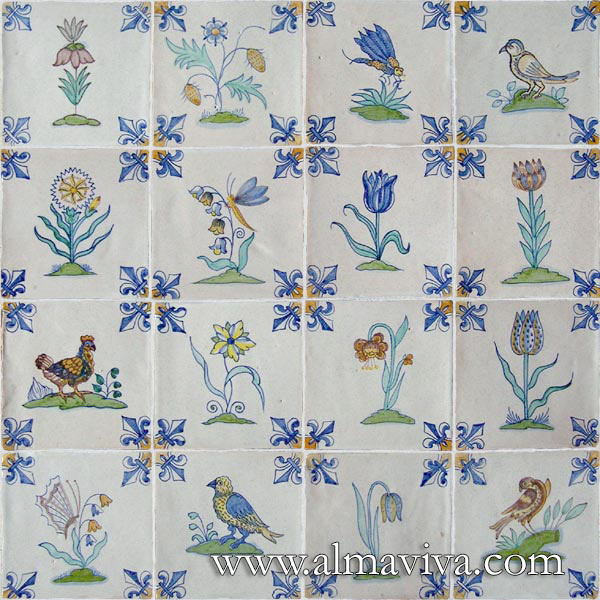
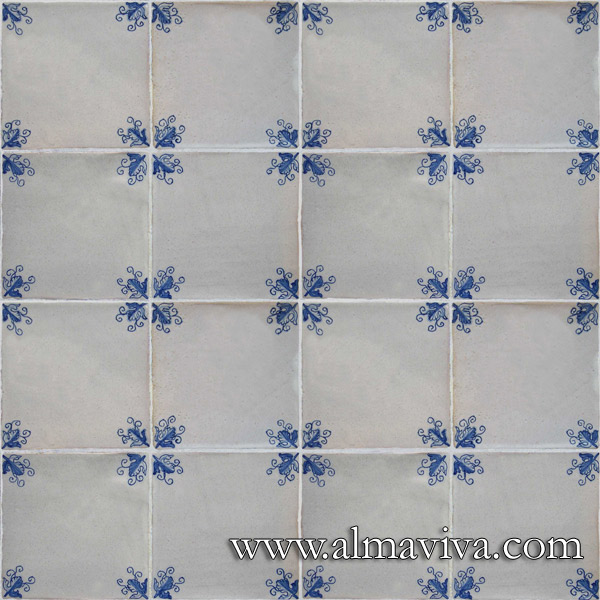
Ref. CD01 - Tiles with corner ''vine leaf'', 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
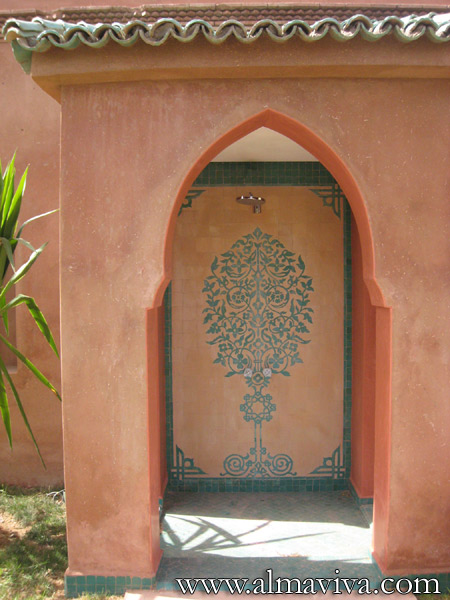
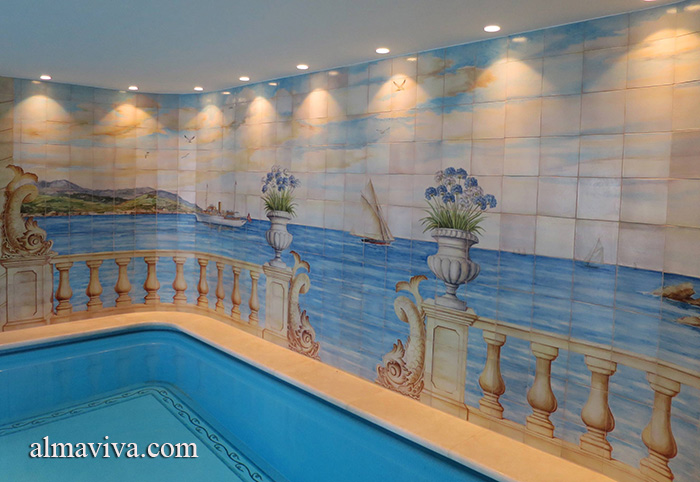
Ref. CD50 - Landscape painted on the walls of an indoor pool
-
View Picture
-

-
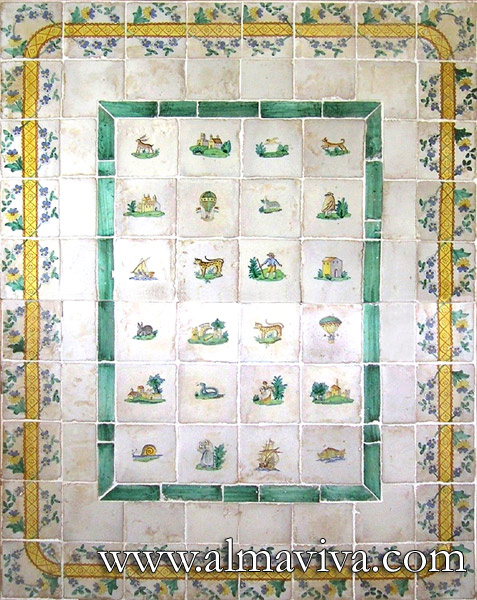
Ref. CD34 - Tabletop. Hand painted tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
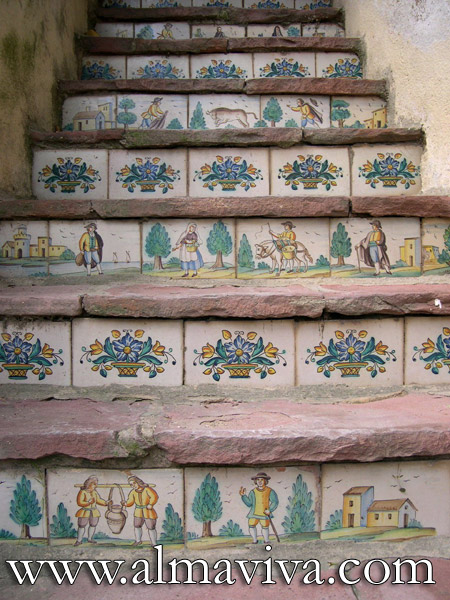
Ref. CD40 - Spanish stair risers. Tiles made to measure
-
View Picture
-

-
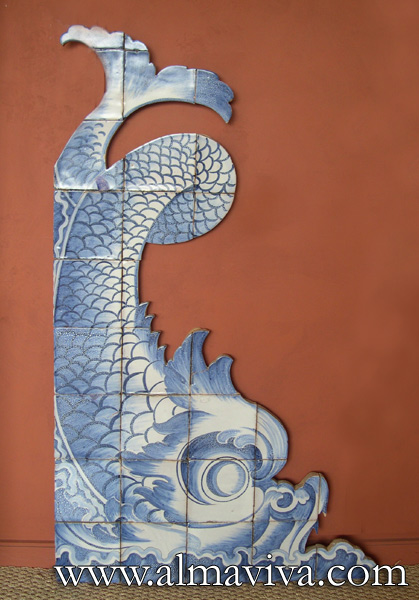
Ref. CD37 - Triton, 125 cm high (about 4,1'), inspired by a fountain in Rome
-
View Picture
-

-
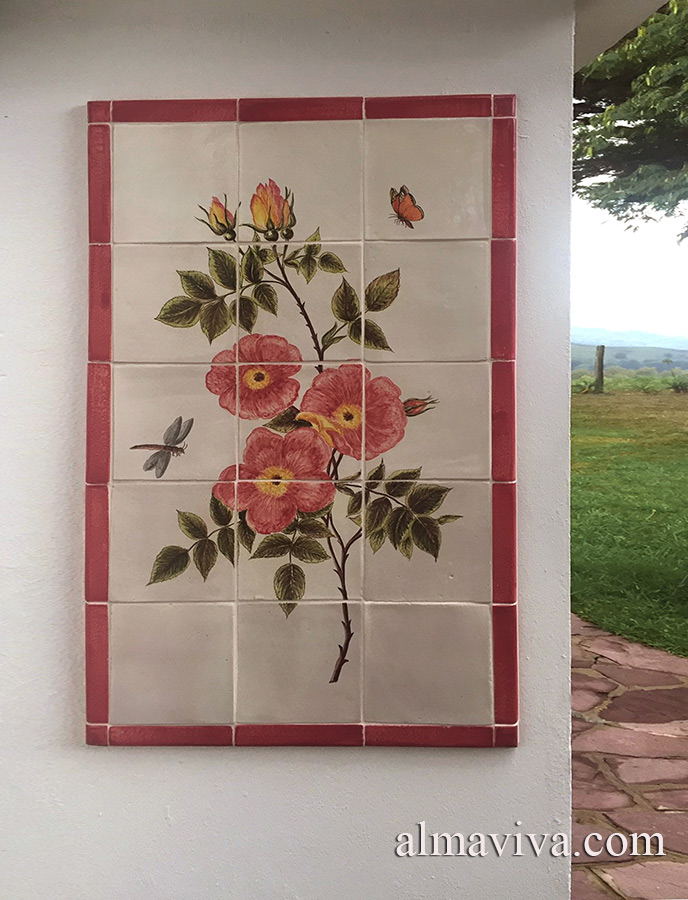
Ref. CD39 - Wild rose decoration inspired by a Rebouté drawing - size 45x75 cm
-
View Picture
-

-
Ref. CD26 - Replica of an engraving on tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-
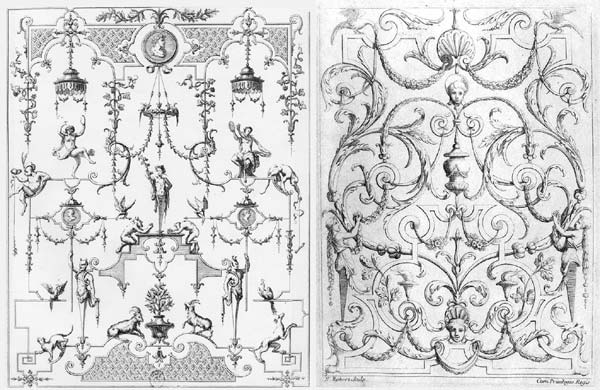
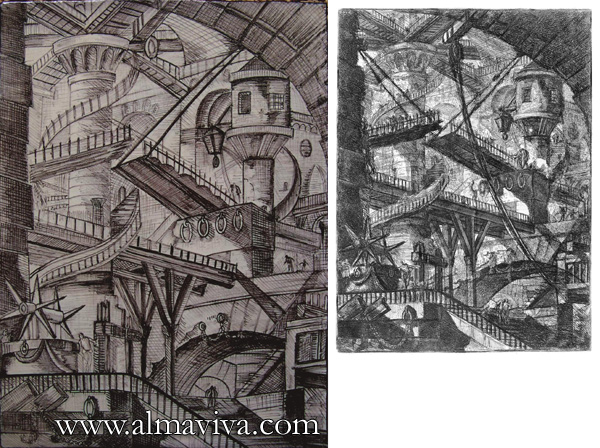
Ref. CD20 - Jail after Piranesi. Dim. 29x40 cm (about 11''x16''). Aside, the Piranesi engraving
-
View Picture
-

-
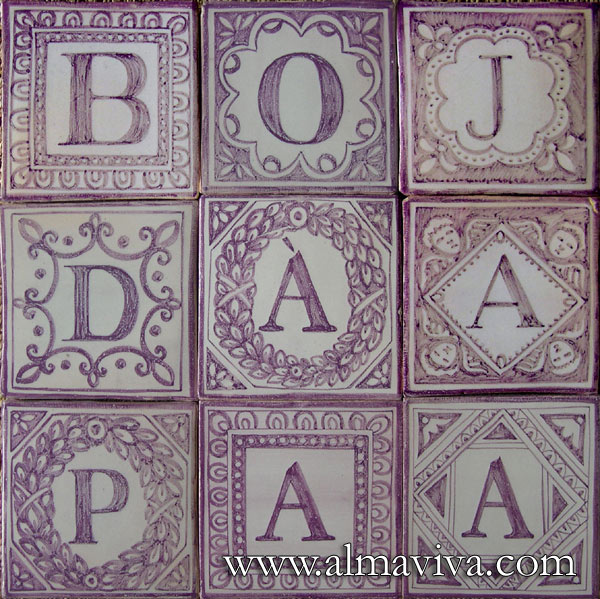
Ref. CD35 - Letters. Tiles 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
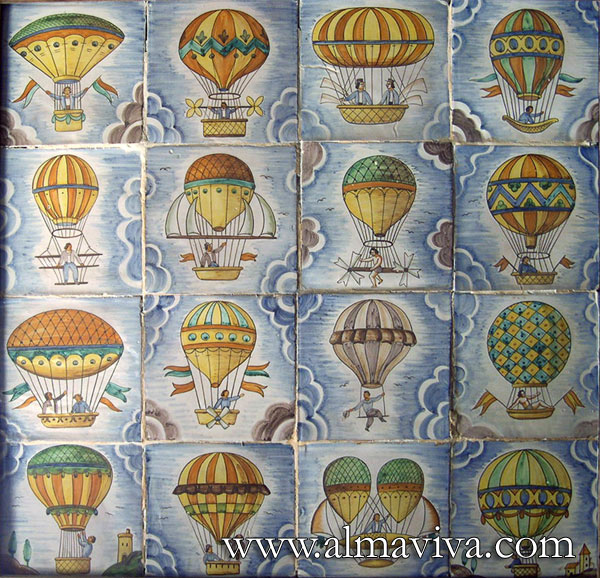
Ref. CD12 - Montgolfier. Tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
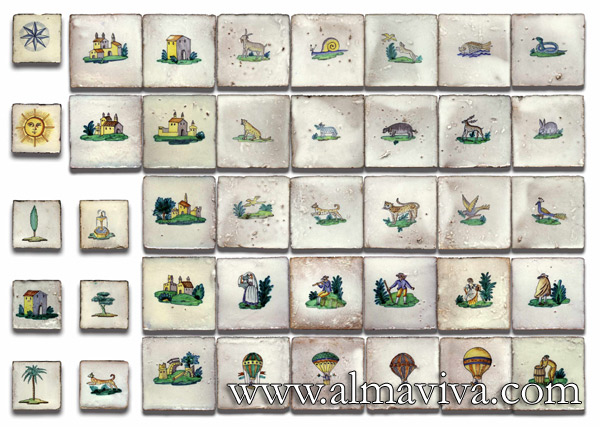

-
Ref. CD05 - Figurines. Tiles 7,5x7,5 or 10x10 cm (about 3''x3'' or 4''x4'')
-
View Picture
-

-
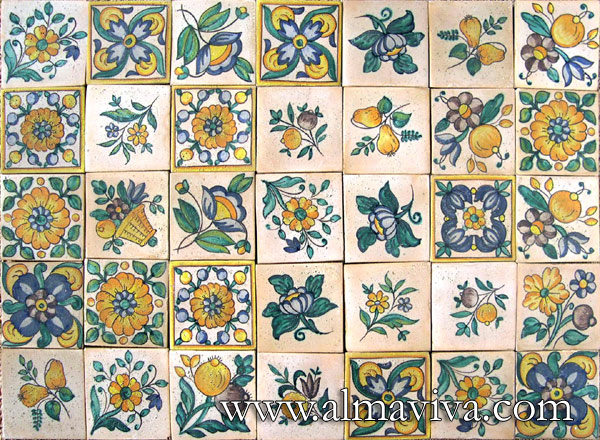
Ref. CD13 - Cabochons flowers. Tiles 10x10 cm (about 4''x4'')
-
View Picture
-

-
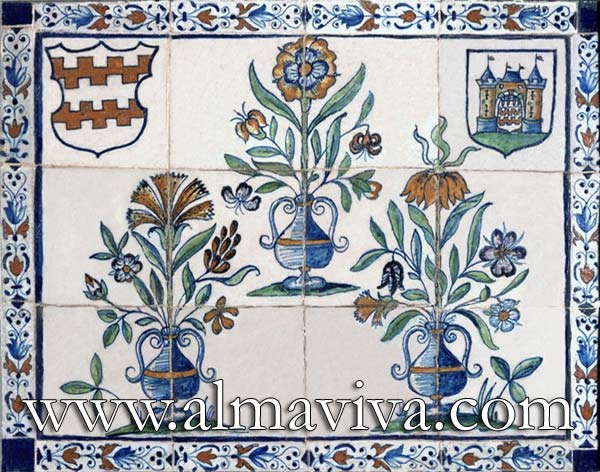
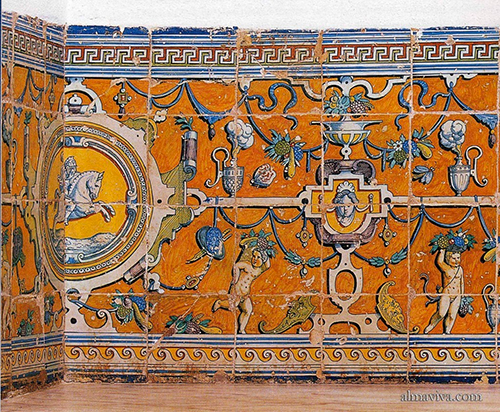
Ref. CD03 - Hunting trophy. Dimension 60x75 cm (about 24''x30'')
-
View Picture
-

-
Ref. CD08 - Spanish kitchen. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
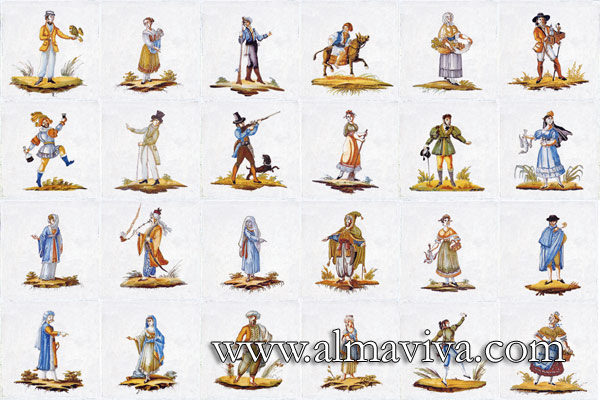

-
Ref. CD47 - Characters. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-

-
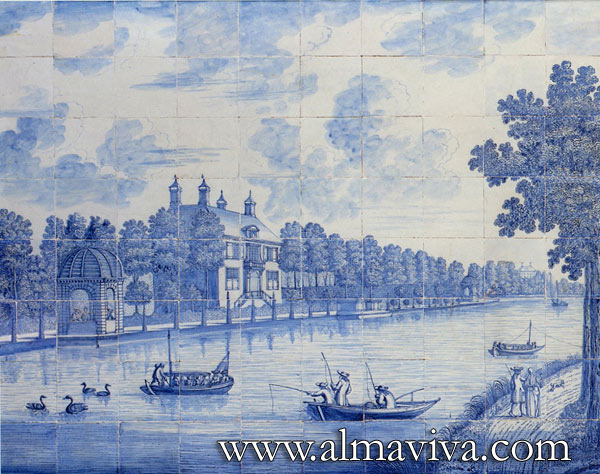
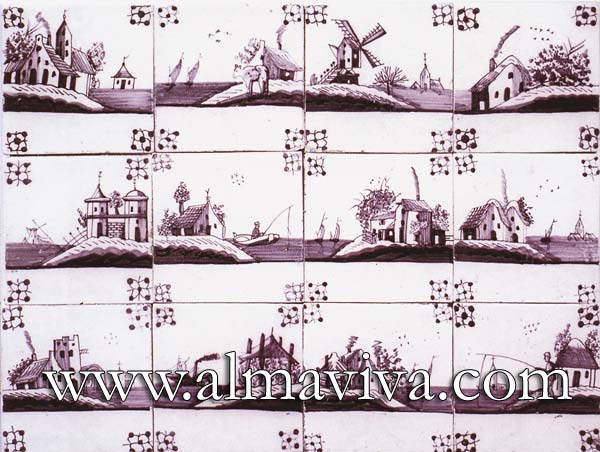
Ref. CD16 - Fishing. Tiles 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
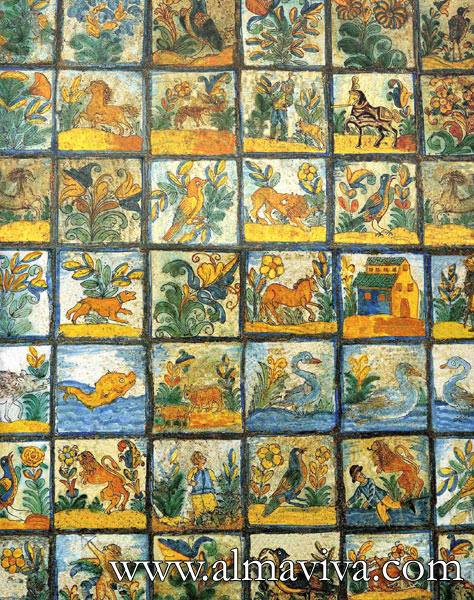

-
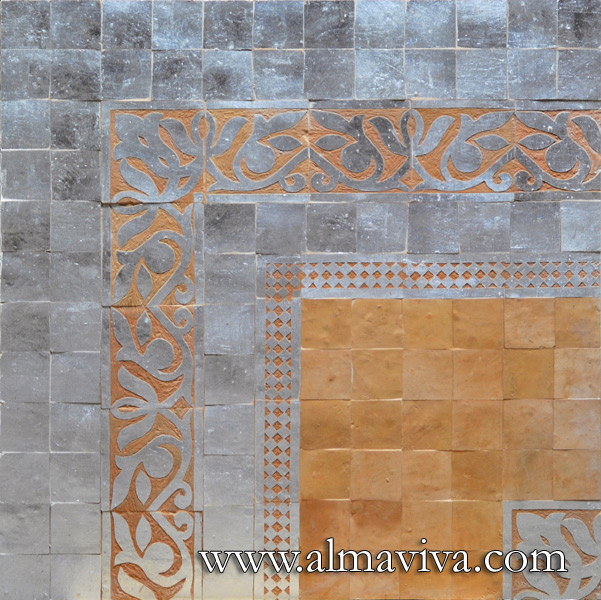
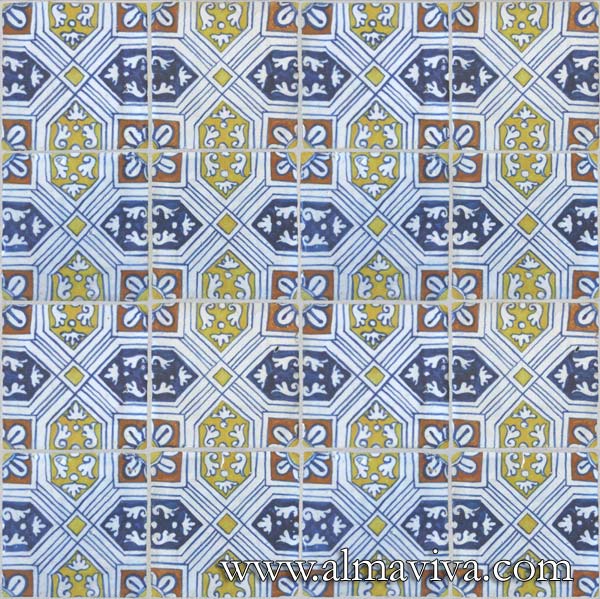
Ref. CD25 - Tiles from Arles (France), 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-

-
Ref. CD30 - Bathroom decorated with handmade tiles in shades of green
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD31 - Zellige in a bathroom. Moroccan stylen tiles
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD32 - Zellige in a bathroom. Moroccan style tiles
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD42 - Terracotta handmade tiles for kitchen
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD28 - Many-coloured shower. Plain tiles 10x10 cm (about 4''x4''), shiny glaze, various colours
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD43 - Another coloured shower, inspired by the Rubik's cube
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD23 - Celadon bathroom (see Keywords). 10x10 cm (about 4''x4'') plain tiles in the shower, alternating with a 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'') decorated tile
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD36 - Turquoise bathroom. Decor alterning 20x20 cm tiles (about 8''x8''), 10x10 cm tiles (about 4''x4''), and a frieze
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD53 - Singerie inspired by Jean-Baptiste Huet painted in the manner of azulejos: the painter and his model
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD15 - Tree on Mont Huang. Dim 80x100 cm (about 31,5'x3,3'). Aside, the pattern that inspired this tile panel
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD21 - Floor handmade tiles inspired from Alice in Wonderland
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD49 - Coral painted on a ceramic panel
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD27 - Tiles 10x7 cm (about 4''x3'') glazed with different whites to give a rich variety of tones and reflections
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD52 - White and blue checkered kitchen credenza
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD48 - Tiles with geometric patterns painted with stencil
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD51 - Bathroom tiles with stripes
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD10 - Matt plain tiles in shades of blue
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD09 - Shiny glazes. Tiles 10x10, or 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 4''x4'', 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD18 - Matt glazes. Tiles 10x10, or 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 4''x4'', 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD04 - Many-coloured wall tiles. 10x10 cm (about 4''x4''), unpolished glazes of different colours
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD11 - Bulb flowers. Each flower measures 15x30 cm (about 6''x12''). Collection of 12 different flowers, created by Almaviva
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD22 - Indian Collection. Patterns inspired from an indian fabric, tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD07 - Butterflies. Tiles 20x20 or 15x15 cm (about 8''x8'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD29 - Fish. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD41 - Interlace 4 different colours. Tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD19 - Commedia Dell'Arte Characters. Tiles 20 x 20 cm (about 8''x8''). Reproduction of 17th c. engravings (see archives)
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD24 - Celadon Interlace (see keywords). Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD33 - Leaves. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD45 - Blue square pattern. Tiles 10x10, 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 4''x4'', 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD17 - Flowers tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD17b - Tiles with corner ''flower'', 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD01 - Tiles with corner ''vine leaf'', 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD50 - Landscape painted on the walls of an indoor pool
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD34 - Tabletop. Hand painted tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD40 - Spanish stair risers. Tiles made to measure
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD37 - Triton, 125 cm high (about 4,1'), inspired by a fountain in Rome
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD39 - Wild rose decoration inspired by a Rebouté drawing - size 45x75 cm
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD26 - Replica of an engraving on tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD20 - Jail after Piranesi. Dim. 29x40 cm (about 11''x16''). Aside, the Piranesi engraving
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD35 - Letters. Tiles 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD12 - Montgolfier. Tiles 15x15 cm (about 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD05 - Figurines. Tiles 7,5x7,5 or 10x10 cm (about 3''x3'' or 4''x4'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD13 - Cabochons flowers. Tiles 10x10 cm (about 4''x4'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD03 - Hunting trophy. Dimension 60x75 cm (about 24''x30'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD08 - Spanish kitchen. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD47 - Characters. Tiles 20x20 cm (about 8''x8'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD16 - Fishing. Tiles 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-
-

-
Ref. CD25 - Tiles from Arles (France), 13x13 or 15x15 cm (about 5''x5'' or 6''x6'')
-
View Picture
-